Mobile App Development vs. Mobile Web Development: When, Why, and How
Mobile web development—optimizing web apps for mobile devices—is necessary for modern apps. Discover the best methods and tools for the development of highly functional, intuitive, and easy-to-use mobile web apps.
Mobile web development—optimizing web apps for mobile devices—is necessary for modern apps. Discover the best methods and tools for the development of highly functional, intuitive, and easy-to-use mobile web apps.
Tomas is a seasoned web developer proficient in both front-end and back-end development with PHP. He excels in responsive web design.
PREVIOUSLY AT

Editor’s note: This article was updated on 08/31/22 by our editorial team. It has been modified to include recent sources and to align with our current editorial standards.
There are 7.75 billion people on the planet, more than 6 billion of whom use a smartphone, according to a recent Statista study. With the increasingly uniquitous nature of mobile computing, mobile web development is more important to the realm of web development than ever before.
As a mobile device user, few things are as frustrating and difficult to fat-finger-navigate as a poorly designed mobile web app or native app.
And as a mobile app developer, few things can be as uniquely challenging as striving to support as wide a range of mobile clients as possible, each of which has its own set of idiosyncrasies. Whether you choose to develop a mobile web, native, or hybrid app, the quest to support multiple mobile browsers and more exotic devices—and coming to grips with various platforms—can be quite a gut-wrenching experience.

As a mobile device user, few things are as frustrating and difficult to fat-finger-navigate as a poorly designed mobile web or native app. And as a mobile app developer, few things can be as uniquely challenging as striving to support as wide a range of mobile clients as possible, each of which has its own set of idiosyncrasies.
Of course, while web and mobile app development are increasingly convergent nowadays, not every developer today needs to worry about supporting mobile clients. But the increasingly prevalent nature of mobile devices and applications strongly suggests that those who don’t need to support mobile clients today will more than likely need to do so in the not-too-distant future. So if you’re not already thinking about mobile app development, you should be.
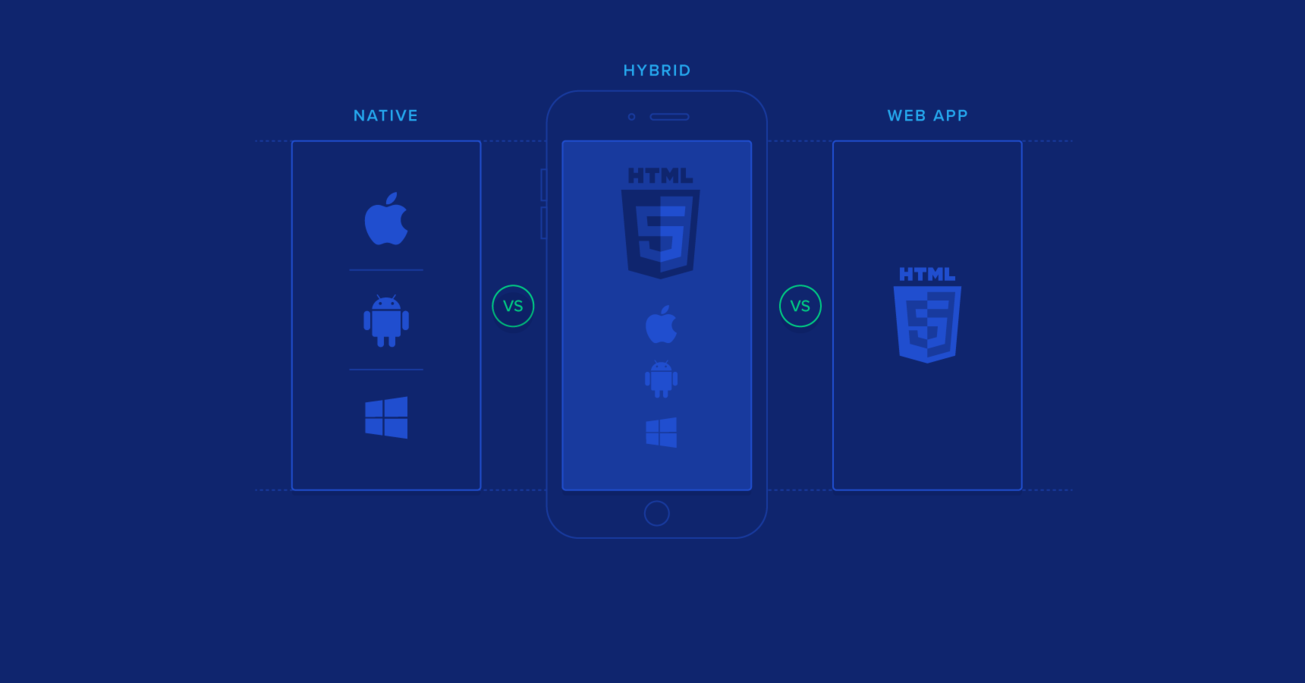
Mobile Web App vs. Native App vs. Hybrid App
As is true with most technology selections, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to the type of mobile app to develop. There are numerous web app best practices to consider, not all of which are technical. Who is your target audience? Are they more likely to prefer a mobile web or a native app? What’s the difference between native and hybrid apps? What development resources do you have and which mobile technologies are they most familiar with? What is the licensing and sales model that you’re envisioning for your product?
Generally speaking (although there are always exceptions), the mobile web app route is faster and cheaper than the native mobile app route, especially when the objective is to support a wide range of devices. Conversely, there may be capabilities native to the mobile device (such as the movement sensor and so on) that are essential to your app but that are only accessible via a native app (which would therefore make the mobile web app choice a non-starter for you).
And beyond the old web apps versus native apps question, a hybrid mobile app may be the right answer for you, depending on your requirements and resource constraints. Hybrid apps, like native apps, run on the device itself (as opposed to inside a browser) but are written with web technologies (HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript) and typically underpinned by a hybrid app framework. More specifically, hybrid apps run inside a native container and leverage the device’s browser engine (but not the browser) to render the HTML and process the JavaScript locally. A web-to-native abstraction layer enables access to device capabilities that are not accessible in mobile web applications, such as the accelerometer, camera, and local storage.
But whatever choice you make—whether it be a mobile web app, a native app, or a hybrid app—be careful to adequately research and confirm your assumptions. As an example, for the purposes of this mobile web development tutorial, you may have decided to develop a native mobile app for e-commerce to sell your products. However, 50% of smartphone users are still more likely to use a mobile site instead of downloading an app—depending on your target market, that number may be even greater.
But whatever choice you make—whether it be a mobile web app, a native app, or a hybrid app—be careful to adequately research and confirm your assumptions.
Then, of course, there are the practical considerations of time and budget. As one of my favorite sayings goes, “Faster, Better, Cheaper: Pick any two.” While time-to-market and cost constraints are of paramount importance in web application development, it’s crucial not to compromise too heavily on quality in the process. It’s quite difficult to recover the confidence of a user who has had a bad first experience.
Indeed, mobile web, native, and hybrid apps are all radically different beasts, each with their own unique set of benefits and challenges. This tutorial focuses on methodologies and tools to employ—and the pitfalls to avoid—in the development of highly functional, intuitive, and easy-to-use mobile web applications.

Mobile Web Development Requires Detailed Planning
Identifying your (or your customer’s) requirements is one of the essential best practices in app development in general, not just web app development. Carefully research the targeted capabilities to determine if they are achievable in your mobile web app. It’s highly unproductive to realize that one or more of your essential client functions aren’t supported when you’ve already invested the time and resources to design the web-based interface and supporting infrastructure.
Another common gotcha for mobile web app development newbies is to assume that web-based code for a desktop browser will work “as is” in a mobile browser. This is not true. There most definitely are differences and, if you’re not aware of them, they can definitely bite you. The HTML5 <video> tag’s autoplay functionality, for example, doesn’t work on mobile browsers. Similarly, the CSS transition and opacity properties are not supported (or at least are not consistently supported) in most mobile browsers nowadays. You will also have problems with some web API methods on a mobile platform, such as the SoundCloud music streaming API that requires Adobe Flash, which is not supported on most mobile devices.
A common gotcha for mobile web app development newbies is to assume that web-based code for a desktop browser will work “as is” in a mobile browser.
A particularly complicating factor while developing mobile web apps is that the lifespan of mobile devices tends to be much shorter than that of desktop displays (the average life span of a cell phone in the US is around 30 months). These shorter device life spans, accompanied by constant releases of new mobile devices and technologies, yield an ever-changing landscape of to-be-targeted devices. While working in a browser does somewhat alleviate this issue by shielding you from a number of device-specific issues, you will still need to design a browser-based view that supports many screen resolutions, as well as adjusting appropriately for landscape and portrait orientations.
Thought needs to be given as well to supporting Apple’s Retina displays (liquid crystal displays that have a pixel density so high that the human eye is unable to discern individual pixels at a typical viewing distance). Several Apple products, including the iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, MacBook Pro, iPad Mini, and iPad Air, offer Retina displays. When optimizing web apps for mobile in particular, it’s important to be aware that a Retina display makes low-resolution images, which are typically served to mobile devices, look fuzzy and pixelation can occur. In these cases, the best app development solution is to have the server recognize that the request is coming from a Retina device and to provide an alternate higher-resolution image to the client.
If you want to use some of the cool HTML5 stuff, remember to verify in advance that the functionality you’re looking for is supported across the device landscape that your customers are likely to be using. For example, in iOS 6 and above, there is no support for the navigator getUserMedia functionality because the camera is only accessible through native apps. Two great resources for checking what’s supported on specific devices and browsers are caniuse.com and html5test.com.
Remember to verify in advance that the functionality you’re looking for is supported across the device landscape that your customers are likely to be using.
CSS3 media queries can also help you provide customized content for each device. Here’s some example code for capturing different device characteristics, such as pixel density, screen resolution, and orientation:
/* For lower than 700px resolutions */
@media (max-width: 700px) { ... }
/* Same as last but with the device orientation on land scape */
@media (max-width: 700px) and (orientation: landscape) { ... }
/* Including width and orientation you can add a media type clause,
in this case 'tv' */
@media tv and (min-width: 700px) and (orientation: landscape) { ... }
/* for low resolution display with background-image */
.image {
background-image: url(/path/to/my/image.png);
background-size: 200px 300px;
height: 300px;
width: 200px;
}
/* for high resolution (Retina) display with background-image */
@media only screen and (min--moz-device-pixel-ratio: 2),
only screen and (-o-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2/1),
only screen and (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 2),
only screen and (min-device-pixel-ratio: 2) {
-repeat;
background-size: 200px 400px;
/* rest of your styles... */
}
}
Optimizing Your Mobile Web Application for Performance
“OMG, this thing is sooooo slow!” As a mobile web developer, those are probably the very last words you ever want to hear from one of your users. Therefore, you must think carefully about how to reduce and optimize each byte and server transfer to reduce the user’s wait time. It’s unrealistic to expect that transfers will always happen on a Wi-Fi network, and you should know that 53% of mobile site vists are abandonded if loading takes longer than three seconds. It is also worth noting that search engines factor load times as part of their calculations of page quality scores.
53% of mobile site vists are abandonded if loading takes longer than three seconds, and search engines factor load times when calculating your page quality score.
As a part of this mobile web development tutorial, here are a few tips that can help optimize the performance of your mobile web applications and minimize latency:
- Image Optimization. Image load time is known to be one of the biggest performance issues affecting page load on mobile devices. Use of online image optimizers, such as Kraken.io, can be helpful in addressing this issue.
- Code compression. Compressing your JavaScript and CSS files, depending on the amount of code you have, can have a significant impact on performance.
- Database queries. Some mobile device browsers don’t accept as many cookies as desktop browsers do, which can result in the need to execute more queries than usual. Server-side caching is therefore especially crucial when supporting mobile web app clients. Remember to employ the appropriate filters to preclude SQL query injection that could otherwise compromise the security of your site and server.
-
Content delivery networks (CDN). If you are planning to provide lots of videos, images, audio files, or other types of media, use of a CDN is highly recommended. Some of the more common commercial CDNs include Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, and MaxCDN. The advantages of using a CDN are numerous and include:
- Improved download performance. Leveraging a CDN’s resources enables you to distribute load, save bandwidth, and boost performance. The better CDNs offer higher availability, lower network latency, and lower packet loss. Moreover, many CDNs provide a globally distributed selection of data centers, enabling downloads to occur from a server closer to the user’s location (resulting in fewer network hops and faster downloads).
- More concurrent downloads. Browsers typically limit the number of concurrent connections to a single domain, after which additional downloads are blocked until one of the previous downloads has completed. You can often see this limit in action when downloading many large files from the same site. Each additional CDN (on a different domain) allows for additional concurrent downloads.
- Enhanced analytics. Many commercial CDNs provide usage reports that can supplement your own website analytics and may offer a better quantification of video views and downloads. GTmetrix, for example, has an excellent website reporting tool for monitoring and optimizing the sources loaded on your site.
Tools for Developing Mobile Web Apps
“The right tools for the right job” is an age-old adage that applies as much to software development as it does to any other domain. This tutorial provides and introduction to some of the more popular and widely used tools for mobile web development, but bear in mind that there may very well be other tools that are the “right” ones for developing mobile web apps, depending on your requirements and available resources.
JavaScript Mobile Web App Frameworks
As mobile web development tends to create many of the same common challenges, such as cross-browser compatibility and inconsistent HTML and CSS in mobile browsers, frameworks have been developed (based on HTML5 and CSS3) that are specifically designed to address these issues and to work as flawlessly as possible on a wide array of smartphones and tablets. Most of these mobile web app frameworks are lightweight, which helps facilitate fast mobile web browsing without compromising the look and feel of your site.
Broadening our view beyond the mobile landscape, if there is a single popular JavaScript framework worth mentioning, it is jQuery. If you’re familiar with the desktop version, I recommend trying jQuery Mobile for your mobile web app. (Note: jQuery Mobile has recently been deprecated.) It has a widget library that converts semantic markup into a gesture-friendly format, making operations easy on touch screens. The latest version consists of a lightweight code base that packs a punch with a lot of graphical elements that really can improve your UI.
Another alternative, Sencha Touch, is rapidly gaining market share as well. It offers excellent performance overall and helps produce a mobile web user interface that largely looks and feels like a native one. Its full-featured widget library is based on Sencha’s ExtJS JavaScript library. (Note: Sencha Touch has merged with ExtJS.)
Here are some key differences to consider when comparing jQuery Mobile and Sencha Touch:
- Look and feel. Generally speaking, the look and feel of a Sencha Touch app is crisper and superior to that of a jQuery Mobile app, but it is important to remember that such responses do tend to be highly subjective.
- Extensibility. jQuery Mobile offers lots of third-party extensions and is inherently designed to be highly extensible, whereas Sencha Touch is much more of a “closed” framework.
- Device support. jQuery Mobile targets a larger cross section of devices than Sencha Touch.
- HTML versus JavaScript. jQuery is largely HTML-centric (i.e., extending and manipulating existing HTML in JavaScript), whereas Sencha Touch coding is entirely JavaScript-based. (This is an example, incidentally, of why it’s important to consider the skill set of your development team when making technology selections.)
- External dependencies. jQuery Mobile requires jQuery and jQuery UI for DOM manipulation, whereas Sencha Touch has no external dependencies.
- Learning curve. Most developers find the ramp-up time with jQuery to be less than that of Sencha Touch, perhaps fueled by the large percentage of web developers who are already familiar with the standard jQuery libraries.
Responsive Frameworks and Mobile Web Applications
There are many responsive frameworks available, with two of the currently most popular being Bootstrap and Foundation. In short, responsive frameworks simplify and streamline web-based responsive UI design and implementation, encapsulating the most common layouts and UI paradigms into a reusable, performance-optimized framework. Mostly based on CSS and JavaScript, many of these frameworks are open-source, free to download, and easily customizable. Unless you have a highly peculiar set of requirements, it is likely that use of one of these frameworks will reduce the level of effort needed to design and implement your mobile web application.
Examining the two leading options, Bootstrap and Foundation, a few of the key differences to consider include:
- Targeted platforms. While Bootstrap does support mobile, tablet, and desktop devices, it is primarily oriented toward desktop use. Foundation, on the other hand, is designed for a variety of screen sizes and types.
- Browser compatibility. Both Bootstrap and Foundation support the latest version of most browsers.
- Diversity of layouts and components. Bootstrap has a significantly larger collection of UI elements than is offered by Foundation.
- Auto-resizing. With Foundation, the grid shrinks and stretches according to the current browser height and width, whereas Bootstrap only supports a pre-defined set of grid sizes based on a standard set of screen sizes.
Debugging and Testing Mobile Web Apps
Debugging mobile web apps can be tricky and somewhat frustrating, especially if you need to scrounge around for different devices to test on or install SDKs for a (typically imperfect) emulation of the targeted client platforms.
In this context, one clear advantage of mobile web application development (as compared with native app development) is that you can utilize standard browser-based developer tools to debug your application. Based on my personal preference for remote debugging, the one I recommend in this app development tutorial is Chrome with its DevTools. Other standard web development options include Firefox with Firebug or Opera’s Dragonfly tools.

Some of the reasons I prefer Chrome with its DevTools include:
- Mobile emulator in Chrome’s DevTools. This alone is perhaps sufficient reason to select Chrome for debugging of mobile web apps. Key features include emulation of touch events, user agent spoofing, network bandwidth throttling, geolocation overrides, device orientation overrides, and CSS media type emulation.
- Interactive editor. Enables the ability to edit JavaScript or CSS on the fly.
- Superior JavaScript debugger. Allows for DOM breakpoints and provides the ability to profile your JavaScript code execution time.
- Built-in JSON and XML viewers. Avoids the need for any plugins to inspect server responses.
- Support for the Android Debug Bridge (ADB) protocol directly over USB. Facilitates easy instantiation of a remote debugging session.
- Dynamic inspection of resources. Allows you to inspect your app’s local data sources, including IndexedDB or Web SQL databases, local and session storage, cookies, and Application Cache resources. You can also quickly inspect your application’s visual resources, including images, fonts, and style sheets.
To test the layout and cross-browsing compatibility of your web app, you can also use some helpful online tools, such as BrowserStack. Just enter the URL for your application and select the browser, version, and operating system, and you’ll get the emulated view (and load speed) of your site in that environment. Another useful tool for this purpose is BitBar.
Choosing Intelligent Mobile Development Solutions
With the continued rapid expansion of the number, variety, and sophistication of mobile devices on the market and in use today, the need for effective, user-friendly, high-performance mobile applications is likely to increase substantially. Being able to develop these applications intelligently and efficiently will continue to be of paramount importance.
Many factors must be considered when choosing between web, native, and hybrid mobile app options for mobile devices. Each has its own advantages, but mobile web apps will often represent your most efficient development (and therefore time-to-market) option. Should you choose to go down that path, I hope this mobile website development tutorial helps get you to your destination successfully and the most directly.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
Understanding the basics
What is a mobile web app?
Mobile web apps are web apps optimized for a good phone experience. They aren’t mobile applications, but websites written in HTML/CSS and run by a browser. While they may be designed to resemble the feel of smartphone apps, they don’t have much in common.
What is a native app?
A native application is an application written for a specific platform, making use of platform-specific APIs.
What is a hybrid app?
A hybrid app is an application written using web technologies and wrapped in a thin native web-browser. A hybrid app can quickly be ported to various platforms where they share the same underlying codebase.
What’s the technical difference between native and hybrid apps?
Native apps are written in platform specific languages using platform APIs, like Java or Kotlin for Android, and Objective C or Swift for iOS. Hybrid apps are written using web technologies like HTML5/CSS and Javascript
Native app vs. web app: What's the impact on user experience?
A mobile web application is a website optimized to be used on a mobile. If done well, the experience is remarkably like a native or hybrid application. As an example, see https://paperplanes.world/.
Why do native apps typically deliver superior performance?
Hybrid apps are usually buggy and slower than native apps, since native apps don’t go through hoops and layers of containers to work. Native apps are much more performant. React Native has managed to change the game, though.
Tomas Agrimbau
Ottawa, ON, Canada
Member since May 13, 2013
About the author
Tomas is a seasoned web developer proficient in both front-end and back-end development with PHP. He excels in responsive web design.
PREVIOUSLY AT