Hiring a Startup CFO: When to Hire a CFO and Why You Need One
For young companies, the value of a full-time CFO is hotly contested. At the debate’s core, is the trade-off between the sheer expense of an experienced CFO at such an early stage (not cheap), and the value said individual posits to confer where growth, strategy, fundraising, and operations are concerned.
Borrowing elements from Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and adapting them for this purpose, Toptal Finance Expert Scott Brown introduces a unique framework for how startups might go about thinking through and making this decision.
For young companies, the value of a full-time CFO is hotly contested. At the debate’s core, is the trade-off between the sheer expense of an experienced CFO at such an early stage (not cheap), and the value said individual posits to confer where growth, strategy, fundraising, and operations are concerned.
Borrowing elements from Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and adapting them for this purpose, Toptal Finance Expert Scott Brown introduces a unique framework for how startups might go about thinking through and making this decision.
Scott has consulted service and manufacturing businesses on capacity planning, incentive plans, business planning, and rolling forecasts.
Expertise
PREVIOUSLY AT

Executive Summary
The Startup CFO Dilemma
- Hiring a full-time CFO at an early-stage startup is a difficult decision, the merits of which are often debated.
- One camp believes that a full-time CFO at a Pre Series-B stage is an unnecessary expense especially given that the company is too young to reap the full benefits of said CFO's range of skills and qualifications.
- The second camp conversely believes that though true—a young company may not necessarily be in a position to exploit a CFO to his/her fullest potential—CFOs bring a deeper, more experienced strategic perspective to structuring, capital allocation, optimization, and fundraising functions for startups, often sufficient to afford said startup a strategic advantage far in excess of the CFO's nominal cost.
When Is a Startup Ready for a Full-time CFO?
- According to Finance Expert Scott Brown, this can and should be determined by weighing the startup's stage against its position on his "Financial Hierarchy of Needs"—a clever adaptation of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs.
- The five stages of Scott Brown's Financial Hierarchy of Needs, from the most basic to the most complex, are as follows: (1) transacting, (2) record keeping, (3) trusted reporting, (4) financial planning, and (5) strategic planning + partnering.
- Popular wisdom dictates that the first two stages require, at most, an in-house or outsourced accountant or consultant, or a fractional CFO.
- It is usually from stage 3 onward, i.e., "trusted reporting," that a CFO starts to become more relevant and almost indispensable.
Other Strategies/Considerations for Making the Hiring Decision
- There are five key questions that every startup must ask and answer as it determines if it requires a CFO:
- Will your startup seek outside investment? If so, it is important that the proper accounting process and policies be put in place.
- How rapidly is your business changing? The faster the pace of change, the more cumbersome and expensive the cost of not adapting your financial and accounting systems in a timely manner; and the more expensive and disruptive it will be to fix further down the road.
- How much financial management skill do you, as the founding team, have and how much time can you afford to spend on this function? Even if you are proficient with accounting and finance, time is always also represent a scarce and valuable resource. "Is this the best use of it?"
- How much financial buffer can you afford to keep ready in case of surprises? With less visibility and planning, surprises are more frequent and larger. You will need a larger cash reserve, better cash management techniques, and a strong cash manager at the helm.
- How complex are your operations? The more complex your financial and general operation, the more skill and experience your business will need to adequately record, report, and plan.
The Great Debate
The value of a CFO for a young company is a hotly contested topic. Many argue that they are unnecessary add-ons and that a small, savvy, well-trained financial team can satisfy the business’s needs. On the other hand, CFOs bring a deeper and more strategic financial perspective that can help companies prepare for the future and optimize their current operations.
For a business to successfully navigate this dilemma, it first requires understanding which roles, needs, and paths the business is likely to encounter. Eventually, most successful businesses will outgrow their initial accounting staff and need greater depth in the ranks as the number of dimensions in the financial function increase. If they understand what their eventual needs will be in advance, there are many ways that businesses can hedge their risks and get what they need, when they need it, without financially overcommitting.
The real question might not be how long can you survive, but how soon will you start benefitting from the contributions of an experienced financial leader. In my 15+ years of experience as a finance director and financial consultant, I have found that the best way to judge whether or not a company needs to hire a CFO is by assessing where they stand on “the hierarchy of needs,” which I explain below. The following analysis will help businesses identify where they are in the hierarchy and be a guide to hiring options that best address their current needs and how to move to the next level.
The Hierarchy of Needs
Much like Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, a business has a hierarchy of financial management needs. These are displayed in the chart below.
Financial Hierarchy of Needs
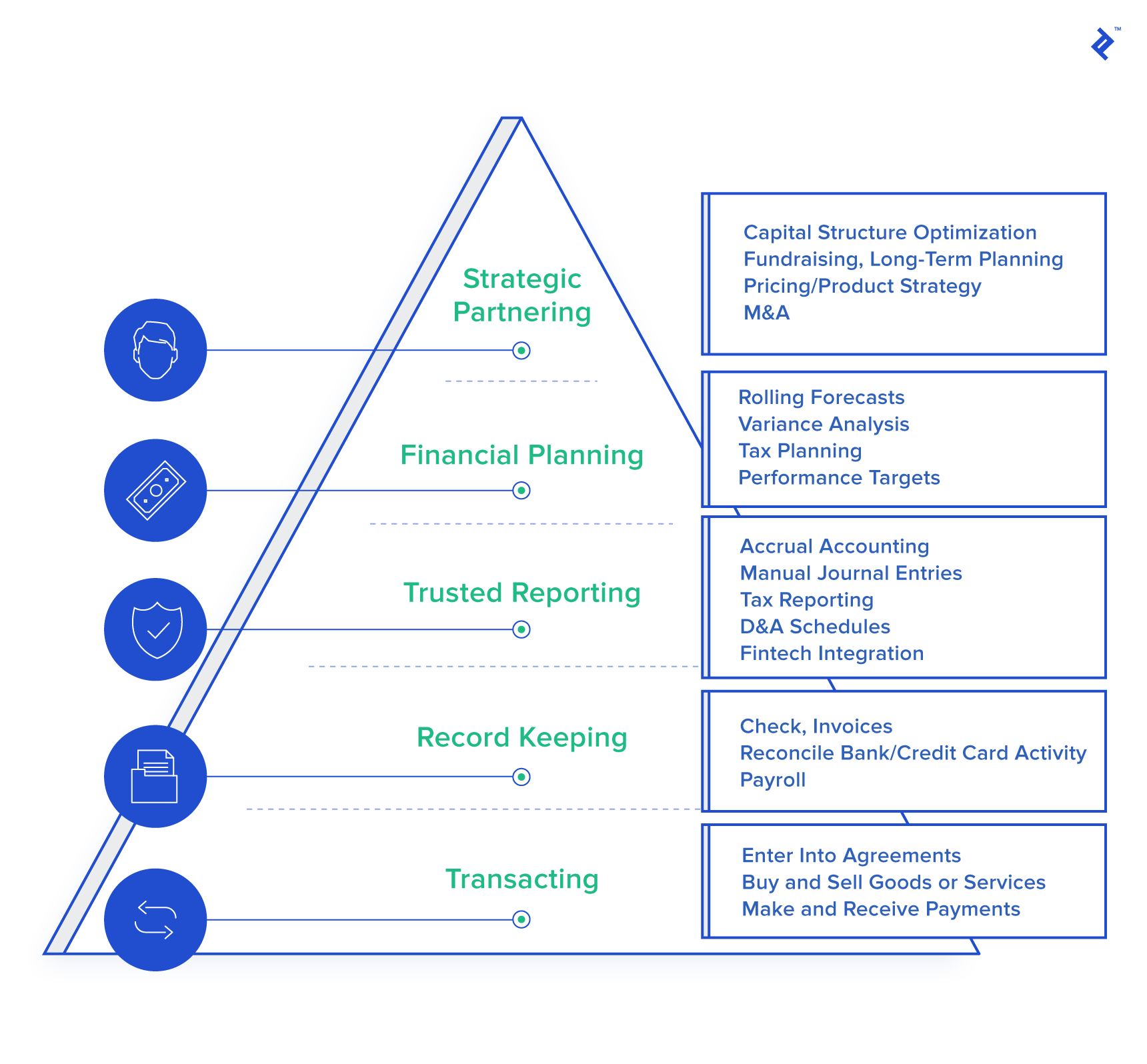
The more basic the needs, the more basic the skills needed to perform them. As the needs progress so do the skills, as well as the insight required to satisfy those needs. The basic needs are clerical and can be met with technical training, but the more advanced needs add a strategic component that is best met by someone with extensive business experience. Different businesses’ needs grow at different rates based on industry, market opportunity, ambitions, and resources. One need cannot be met if a preceding need is left unmet.
Level 1: Transacting
The most basic need of a business is the ability to conduct transactions. By conduct transactions, I mean buying and selling goods and services and entering into contracts.
Basic transactions require basic record keeping—what I refer to as checkbook accounting. This can be done by anyone in the business and requires no accounting or financial knowledge. It usually involves a business only recording transactions in the checkbook and then using the change in the opening and ending balance(s) to judge its success and financial health.
The advantages of checkbook accounting are clear. It’s cheap, and it requires little effort. It can be done quickly, and it doesn’t require a specialized resource to do so. Businesses that are just getting started are therefore likely to resort to this type of activity, which makes sense. Nevertheless, even with only basic transactions, many businesses find themselves in serious trouble because they have conducted such transactions without graduating from using checkbook accounting to using “real” accounting.
Level 2: Record Keeping
Real accounting is built around the need to record transactions correctly and can be performed by either a bookkeeper or, as the transaction complexity increases, an accountant. An owner can certainly fill this need as time and skill allow, but should be aware of the opportunity cost of doing so.
The role of a bookkeeper is to record activity from transaction sources, such as bank balances and inventory. Usually, a bookkeeper requires management and is overseen by an external accountant or the business owner. Using an outsourced bookkeeping service gives the business better flexibility but requires more detailed communications and review.
While both a bookkeeper and an accountant are focused on recording historical transactions and activity with varying degrees of accuracy and compliance, an accountant differs from a bookkeeper in that they are trained to higher professional standards. This training and education gives them the skills to better guarantee that the completeness and timing of financial activity has been properly recorded. Accounts prepared by an accountant should be prepared in compliance with GAAP and should meet the more stringent reporting requirements of a company that will one day seek external financing.
I recently worked with a client who not only had very good, GAAP compliant record keeping for an early stage business but also surprised me by having a complete catalog of all of their contractual obligations. While there weren’t many, their founder was a former CFO and knew that when the time came, lenders and investors would require full disclosure of all contractual obligations. By recording their contractual transactions from the start they are in much better shape for an eventual capital raise.
For businesses that want greater oversight without significantly greater costs, it often makes sense to use an external resource to periodically review the bookkeeper’s work, especially if, unlike my client, the leadership doesn’t have accounting experience. This can be bundled with tax preparation work or by a retained fractional CFO.
Fortunately for cost-conscious firms, the ability to capture transactions has changed significantly in the past decade. No longer is it a manual data entry world. Much of this has now been replaced by software applications and other IT resources. This, of course, has implications on a business’s cost structure (the point being that software replacing labor helps to save costs).
Generally speaking, businesses that are at this level in the Hierarchy of Needs can get away with not having a CFO. After all, the principal requirement is just a correct recording of the transaction(s) that the business is performing. Since this task is still fairly basic and can be done either with in-house trained labor or by hiring part-time external labor, it will likely not require the services of a more expensive, dedicated CFO.
The Illusion of Fintech
As financial and operational data is drawn from many sources into hosted accounting systems, the focus has shifted from manual data entry to ensuring and assessing the quality of the data and how it is captured.
However, when not properly implemented, these software applications can mislead businesses into believing that just because the data is in the system, it is correct, when in fact it isn’t.
As a result of this, the accounting systems and the operational interfaces need to be set up by someone with a strong understanding of the accounting principles. Quickbooks, one of the most popular accounting software solutions around, says so itself: “As your business—and revenue—grow, managing your financials may become a task you don’t have the time or knowledge to manage. Specifically, when it comes to avoiding legal and compliance issues, accountants can be worth their weight in gold.”
This is a time where it would make sense to a company to pull in an external financial consultant to ensure that the applications are integrated properly and that there are policies set up to ensure that the usage of the applications supports the financial reporting function.
Another company that I recently consulted with needed to fix a faulty inventory tracking software implementation. The company had experienced significant growth in its first four years of operation but had failed to properly set up sales tax schedules and taxable items. This resulted in incorrectly reporting a rapidly increasing amount of sales tax over a period of years.
I worked with the business to fix the implementation, and file the corrected returns. Unfortunately, for many months, the cost of the penalties and interest exceeded the actual sales tax due. While fixing the implementation, other opportunities for improvement were identified and implemented. The client is now able to better report real-time profitability by product line through their accounting system. It has also used this to make adjustments to its product mix at significant savings to the business.
Nevertheless, the project served as a great example of the potential problems related to fintech. Even an adequately connected IT-based financial system will require a regular review of the data and account reconciliations. These activities require not only a good understanding of accounting but also an ability to assimilate operational data into the financial records.
Level 3: Trusted Reporting
With transactions being properly accounted for, a business can start reporting on the activity of the business. The key difference here is that the reports start to take the shape of business lines (e.g., the sales department’s revenue and costs) or specific business tasks (e.g., customer service), as opposed to simply just reporting the transactions of the business (e.g., revenue).
Again, fintech has made it so that comprehensive reporting is more affordable and robust than ever before. Business schools have been evolving in recent years to ensure graduates have a strong understanding of fintech and its myriad applications. Dedicated courses have even been popping up.
That being said, it is important to know how the reports are going to be used prior to putting in place a reporting system. Although accuracy is always a requirement, reporting for internal purposes doesn’t need the same approach and level of review as reporting used for external purposes. Depending on how the activity was captured, the reports can be presented in a number of ways but always with the caveat: “Garbage in = Garbage out.”
The main purpose is to communicate transactional information at the appropriate level for the audience in question. If this can be accomplished by the bookkeeper and/or accountant, their job is done. If not, the business will need to have someone who can properly convert the accounting information into meaningful communications.
Not having a single source of data leads to either capturing less than 100 percent of what was intended or, in some cases, duplication and more than 100 percent of activity gets reported. Successful reporting needs to be thorough, accurate, and complete, especially as these early-stage businesses are preparing to raise Series A funding.
It is usually at this stage in the Hierarchy of Needs that a CFO starts to become more relevant. After all, taking the records of transactions and slicing and dicing them to start to satisfy and guide the business’s day-to-day involves deeper knowledge and judgment. Nevertheless, one common option here is to seek part-time help from an external CFO. In my experience, this is usually when I get involved with the business. It is also where I find I can start adding the most value.
Financial Reports, Ends or Means?
Reports on their own are not the end goal. They are supposed to be a means with which to understand business activity. For example, it’s not enough to know that the ending cash position for the period changed by a certain amount if you can’t identify which activities drove the change.
Earlier on in my career, I worked with a client who didn’t understand that being a seasonal business caused sizeable fluctuations in the working capital needs as accounts receivables and inventory positions grew during peak periods. Their bookkeeper provided them with cash balance reports but with no explanation. I worked with them to identify metrics, such as inventory turnover and days sales outstanding that they could track to give a better reflection of how the business was doing and to also help forecast future cash positions.
As mentioned, reports created for external use serve a different purpose than management reports, which are created for internal use. If they were created for internal use, they are the means by which the business learns about its activities and uncovers opportunities that can be acted upon.
A business is more likely to thrive when reports are generated by a person who is skilled at analyzing and interpreting the financial data contained in the reports. This person can identify when standard reports need more details and can create ad hoc analyses when it makes sense. Knowing when to take this next step and how to go about it only comes with experience.
In particular, businesses experiencing rapid change cannot afford to skip interpreting the information contained in the financial reports. In fact, they should be strongly relying on these (and on things such as dashboards of KPIs) to help them navigate their way. But creating meaningful dashboards is not as simple as it sounds. It requires understanding what factors drive the business and what signals they send off. Some KPIs may be purely financial whereas others might be a mixture of operational and financial data. An experienced finance leader will know how to pull together this critical information or direct others in doing so.
Level 4: Financial Planning
With an accurate record of historical activity and analysis of the factors that influenced successes and shortcomings, a business can use the information gathered to develop financial forecasts. As the cliché goes, “You can’t know where you are going until you know where you have been.”
The process of creating a forecast is nothing like the steps for recording accounting activities and requires a different set of tools and skills.
A forecast ideally would be a rolling forecast and should always be projecting 12 months out at any given time. This is especially true for seasonal businesses. The forecast should include three financial statements: profit and loss, capital expenditures, and cash flows. Leadership can then work with the rest of the business to ensure that the business has sufficient resources to meet its goal-based needs. The finance team seeks to scale business resources to meet the plan with no more and no less than what is needed so that opportunities and/or resources are not wasted.
Companies that are at this level of the Hierarchy of Needs will almost certainly require a CFO. As mentioned above, a part-time CFO may be enough, but there would need to be a close working relationship and collaboration with management in order to achieve meaningful and, hopefully, accurate financial forecasts.
Level 5: Strategic Partnering
Businesses that aspire to continually grow and improve will seek the most from their financial management team. The ultimate deliverable of the financial management team is strategic partnering, where the financial function partners with other areas of the business and is an integral part of the strategic planning process. This can only be achieved once the business understands where it has been and where it is heading.
Strategic vision includes long-term pricing decisions, scenario analysis, international expansion, acquisition decisions, as well as many other higher level decisions. Strategic partnering results in the assimilation of new frontiers into the long-term financial goals of the business.
A seasoned finance leader who can partner with the business to create a financially viable strategy is a must at this level.
Choose Lean Finance
In today’s business environment, lean organizations are proving that with the right financial discipline, companies can achieve significant results with far fewer resources than what was once possible.
As noted by Christian Gheorghe, the CEO of Tidemark, “Even a mid-level finance pro can move an organization’s planning, budgeting and forecasting processes beyond Excel spreadsheets so managers have the data and analytics needed to understand those ‘what-if’ scenarios and utilize predictive analytics and forecasting.”
By increasing the yield from labor and financial resources, high growth businesses are more agile and better able to respond to changing business conditions. While FinTech does have limitations, it is becoming a tremendous enabler. It, for instance, gives the business the ability to embrace remote working which allows for it to retain higher quality talent at a lower cost of compensation. Software that manages accounting and finance better supports the use of outsourced shared service centers.
Collaborative technology has made it easier for businesses to hold off on hiring full-time finance resources while still having access to a worldwide pool of highly talented individuals. Businesses can now engage fractional CFO’s and advisory boards and get around to hiring a full-time CFO later, while still meeting their needs for more sophisticated financial leadership.
That being said, as concrete milestones approach, a seasoned finance leader, who can create a financially viable strategy, is a must. This is especially true when a business is trying to rapidly grow through a series of external financing rounds. While advisors, VCs, and consultants can get a company through early-stage investments, waiting too long can result in the CFO not having sufficient time to learn the business before pre-IPO activity begins.
Finding the right CFO, who is willing to join the venture, can take some time. Paul Holland of Foundation Capital said that “It’s not uncommon, for it to take several months to execute on a high-quality CFO hire. The ideal time frame in which to make that hire is 12 to 18 months before the IPO.”
Another challenge for companies without a CFO in this environment is to keep track of regulation. As an example, ASC 606, when it goes into effect, will require businesses with external investors to report revenue differently from how they may have traditionally done.
In conclusion, while hiring a CFO need not be a top priority at the earlier stages of a company’s lifecycle, if the business continues to grow and its ambitions also increase, a CFO is required to effectively manage the business’s growing needs.
What Capabilities Should You Solve for When Hiring a Startup CFO?
As just explored, the decisions of whether and when to hire a startup CFO is a tricky, amorphous one, dependent on variables that only the startup’s founder and board can weigh and assess. Once the decision has been made, however, most first-time founders often find the process difficult to navigate. Specifically, without prior knowledge of the intricacies of a CFO’s role, responsibilities, and qualifications, most startup founders often find themselves feeling their way through the dark, for months on end.
My first point of advice here is to pick/appoint an advisory board member with deep experience in this arena. Specifically, an individual who is both close enough to you and your startup to accurately assess its stage and needs (both current and forward), and one with the experience to match those with the appropriate qualifications, temperament and skill/risk profile of a potential CFO. Navigating this process alone too often leads to costly mistakes—especially given that good CFOs don’t come cheap or worse, this can be destructive in an extreme downside case.
Beyond the direct guidance of an advisor, the following are a few requisite qualifications/capabilities derived from my personal experience that you should solve for when assessing your available pool of CFO candidates:
- Forecasting, Modeling and Analysis Capabilities: Beyond the usual certifications and experiences associated with the role, such as an MBA or CPA, your CFO must be well versed in budgeting, forecasting, financial modeling, and returns-profiling analyses. These skills are a minimum requirement for any effective/value-adding finance operation.
- Strategic Judgement and Vision: Your CFO must also at a minimum be forward-looking and be a driver of strategic thinking and growth alongside the founders and board. Where possible, they should have a demonstrable track record for value creating initiatives or experiences that they can point to, and should come to the interview with a clear view of what they believe the possibilities are for your business and associated execution strategies. Solving for these qualities will inadvertently weed out the risk-averse, innovation killing, “no-men/women” that are so often associated with the CFO title.
- Risk Assessment + Mitigation Skills: Startups, on their best day, are turbulent, unpredictable vehicles, constantly flying in the face of a sea of destabilizing forces. As such, a large part of your CFO’s job will be to assess and manage risks, a resource-scarce financial position, while keeping one foot on the gas.
- Balance, Judgement and A Strong Moral Compass: A great CFO must also come with a healthy growth orientation, a clear sense for the levers that will drive profitability, and must also be a compelling storyteller with numbers and his/her analysis. These qualities will be most critical during periods of fundraising and investor reporting.
- Ability to Build and Manage an Agile Infrastructure: A near-final capability of any startup CFO is to be able to build a lean financial organization from scratch, especially from within a dynamic, fast-evolving environment.
- Intellectual and Functional Dexterity: As a final point, and more of a “nice to have” than a must, is that your CFO should, depending on your startup’s stage, be a jack-of-all-trades or generalist athlete who can fill multiple roles within the company. This will help improve the ROI of the individual in question, especially if this is the specific point of deliberation for whether to hire or not at this juncture.
Five Questions to Ask When Building a Finance Function
Capabilities aside, below are a number other (key) considerations that I encourage every startup founder to ask in deciding how/when to staff his/her finance function:
- Will you be seeking outside investment? If so it is important to put the proper accounting process and policies in place as early as possible.
- Is your business rapidly changing? A historically focused transactional mindset will be limited in its ability to help identify opportunities and threats. Additionally, as the business changes, the accounting processes too may need to change.
- How much financial management skill do you have and how much time can you afford to spend on this? Even if you are proficient in accounting and finance, every hour you spend on the finances is at least an hour you can’t spend doing what you do best.
- How much financial buffer can you afford to keep ready in case of surprises? With less visibility and planning, surprises are more frequent and larger. You will need a larger cash reserve.
- How complex are your operations? Like machines and most everything else, the more complex your operations and finance the more skill and experience your business will need to adequately record, report, and plan.
The Right Startup CFO
Ultimately, the timing for any given startup as to whether it should hire its first full-time CFO is a decision that only the company’s founder and board can make. But as succinctly reduced by Ian Brooks, the appointment of one’s first CFO often represents a strategic, managerial, and operations tipping point for the company, indicating it is ready for a deeper, more sophisticated and specialized level of management, strategic planning, and execution.
As you embark on your process, remember that the right startup CFO will have the capacity to navigate between strategy and execution, bring strategic direction and passion to the company, and also add value beyond his/her specific function or role as the company scales.
Happy hunting.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
Understanding the basics
What is a chief financial officer responsible for?
A CFO is responsible for the following: the analysis, review, and reporting of financial data/financial performance; managing financial planning and financial risks; preparing budgets; and monitoring expenditures and costs. Further, they are the key financial spokesperson for the corporation.
Who do CFOs report to?
The chief financial officer (CFO) generally reports to the CEO of the company and/or its board of directors. The CFO is part of the senior executive team (C-Suite) who, together with the CEO, COO, and other C-level executives, are responsible for executing the strategic vision approved by the board.
Do you have to have a CPA to be a CFO?
A certified public accountant (CPA) is a financial advisor who is certified, has met work experience requirements, and undergoes continuing education. Traditionally, a CPA early in one’s career was an unspoken requirement for the CFO role. Today, an MBA and simply “relevant experience” is often sufficient.
Scott Brown
Atlanta, GA, United States
Member since September 23, 2016
About the author
Scott has consulted service and manufacturing businesses on capacity planning, incentive plans, business planning, and rolling forecasts.
Expertise
PREVIOUSLY AT


