Ask a Cybersecurity Engineer: Trending Questions About AI in Cybersecurity
In this ask-me-anything-style Q&A, leading Toptal cybersecurity expert Ilia Tivin responds to colleagues’ questions on AI in cybersecurity and provides data and network protection tips and best practices.
In this ask-me-anything-style Q&A, leading Toptal cybersecurity expert Ilia Tivin responds to colleagues’ questions on AI in cybersecurity and provides data and network protection tips and best practices.
Ilia is a cybersecurity professional and developer with wide-ranging experience in the government, defense, manufacturing, and finance sectors. A former cloud security architect at Hewlett Packard Enterprise, he now advises executive clients on planning, prioritizing, and executing strategic security initiatives.
Previous Role
Senior Security ConsultantPREVIOUSLY AT


Having worked in a variety of cybersecurity roles for large companies and startups for two decades, Toptal cybersecurity advisor Ilia Tivin has a deep understanding of the field—past, present, and future. This Q&A is a summary of a recent ask-me-anything-style Slack forum in which Tivin fielded questions about artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity from other Toptal engineers and security professionals around the world.
Editor’s note: Some questions and answers have been edited for clarity and brevity.
Current and Future Uses of AI in Cybersecurity
Do you think modern cybersecurity requires AI solutions?
—K.S., Montreal, Canada
Yes, I do think AI will be required in the future. To be frank, AI’s capacity for creating exploits is fairly weak today. But that is going to escalate over time—and so should our defenses.
Did you ever encounter a business case in which AI was used to find security breaches?
—J.O., Fortaleza, Brazil
The answer depends on how you define a security breach. AI that is properly programmed to search and sift through code can definitely be used to identify vulnerabilities. You can also have AI generate very persuasive phishing emails that incorporate specific details relating to your organization. I haven’t yet seen anything outside of phishing emails, but that doesn’t mean it hasn’t happened.
What are the downsides of AI in cybersecurity?
—K.B., Bergerac, France
The downsides of AI in cybersecurity are the same as the downsides of AI in every other field. When we apply AI, we delegate a layer of decision-making to a robot. But sometimes we cannot fully understand how the robot arrives at its decisions. If AI decides wrongly about security automations, checks, or compliance, for example, it can lead to significant regulatory fines, security compromises, or loss of intellectual property.
What new cybersecurity risks might modern AI (e.g., generative AI) create?
—R.L., Lake Oswego, United States
A risk that comes to mind is overreliance on AI, even when it benefits from the latest developments. As developers move to use AI to code, as well as to check their code using that same AI, they may inadvertently introduce security vulnerabilities to the code.
How might AI improve cybersecurity in the future?
—N.H., Tuzla, Bosnia and Herzegovina
First, AI will hopefully stop supplying wrong information and errors. I see a move toward more automation worldwide. I also predict the enhancement of inspection methods, contingent on the countries and jurisdictions in which the various AI companies operate. Inspection enhancement is less likely to be implemented in Europe, due to its strong regulatory frameworks.
Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
Upsides | Downsides |
|---|---|
|
|
AI in Cybersecurity Examples
Do you use any AI cybersecurity tools and, if so, which ones would you recommend?
—M.D., Seattle, United States
To complement the protection afforded by clients’ standard security products, I use the AironWorks phishing simulation platform, where customized phishing simulations are generated for organizations to check the preparedness and security awareness of their employees. But currently, from a testing perspective, I don’t think that AI is well positioned to be of much help in cybersecurity. Sure, all the big companies claim to have adopted AI for cybersecurity in their product offerings, but the extent to which it is usable varies.
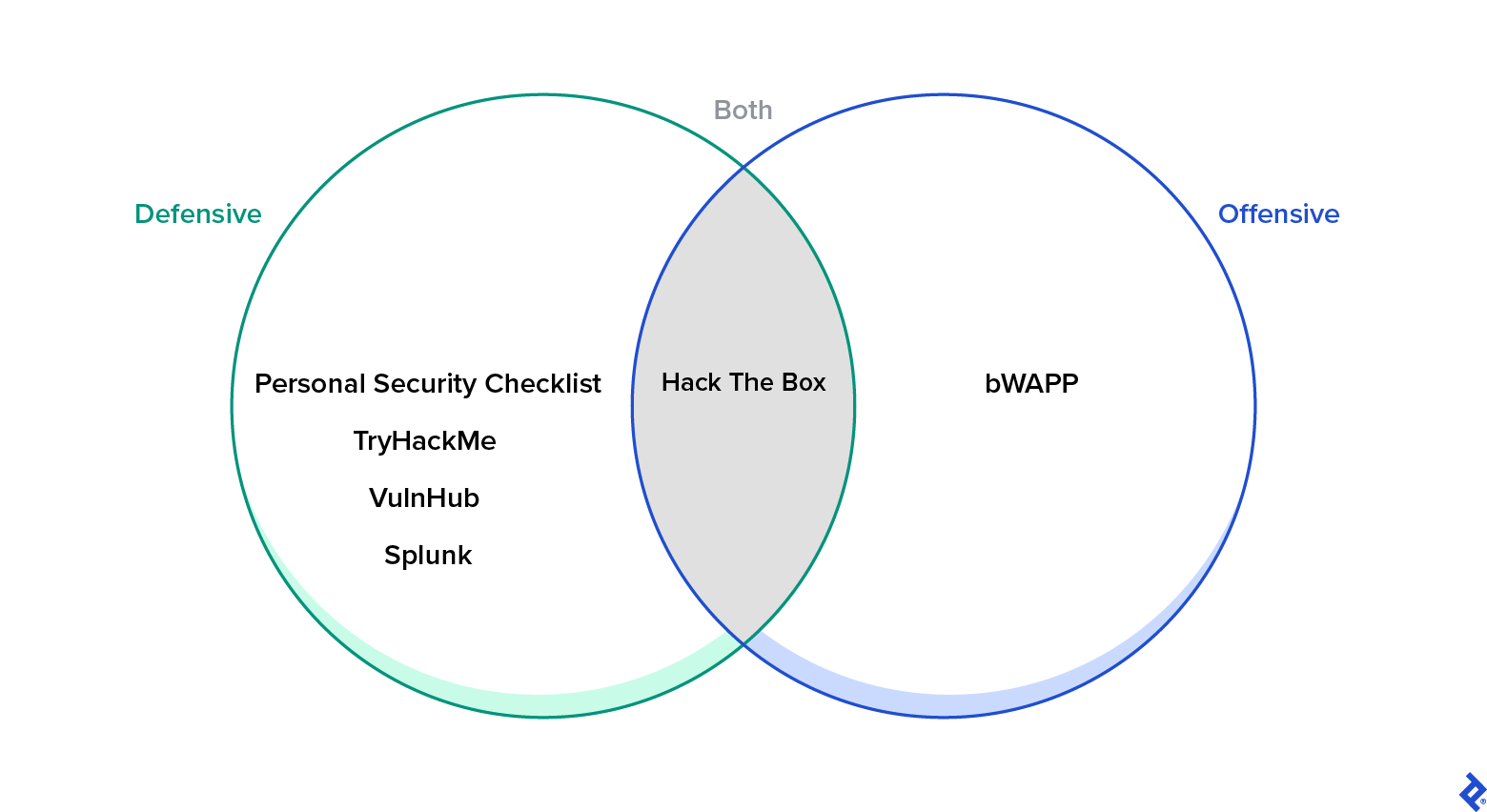
Can you suggest a fun website where security hobbyists can play around with and discover different topics of offensive or defensive security?
—J.O., Fortaleza, Brazil
I, for one, am a big fan of personal security. From a defensive perspective, I always recommend the Personal Security Checklist, a GitHub list of 300-plus tips for protecting digital security and privacy. You can use TryHackMe as a way to get started in security, or even compete in some of its online challenges. VulnHub is awesome even if it’s not regularly updated. Challenges at Splunk—which appears ready for a refresh—come to mind. From an offensive perspective, bWAPP is a good Docker container that allows you to try to exploit a web application for yourself. And there’s also Hack The Box, which includes both defensive and offensive elements.
I hear conflicting perspectives regarding Mac security: Some say that Mac is already secure, while others feel that you can’t be too careful. What’s your opinion?
—M.Z., Santa Clarita, United States
Well, there are significantly fewer Mac users than PC users, which can explain why a majority of cyberattacks are aimed at PCs. However, on average, Mac users spend far more money on their computers than PC users do—so you can see how Mac also makes for a favored target. Judging by the many OS security fixes released lately, it looks to me—and also to Wired, which published an article on this topic—as if Apple agrees that increased Mac targeting is a real possibility.
Would you recommend enhancing security on Mac computers with antivirus tools like Avast, or are these a waste of money?
—M.Z., Santa Clarita, United States
You can always go free with ClamAV in combination with keeping your software updated. Also, Microsoft Defender is now available for Mac.
The editorial team of the Toptal Engineering Blog extends its gratitude to Marco Jardim for reviewing the technical content presented in this article.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- Cybersecurity in Higher Education: Problems and Solutions
- Cybersecurity: What Every CEO and CFO Should Know
- The Shadow Pandemic: Ransomware’s Present and Future Dangers for Corporations
- How Machine Learning Can Enhance Cybersecurity for Autonomous Cars
- Cybersecurity Spotlight: Preparing Your Organization for Deepfake Voice Clone Fraud
Understanding the basics
What is the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing cybersecurity?
AI’s role in enhancing cybersecurity can relieve cybersecurity personnel of repetitive and mundane tasks, accelerating the response times to threats.
What are the cybersecurity concerns with AI?
Accuracy is a concern as code written by AI that is not fully inspected can lead to improper and insecure coding practices that can, in turn, lead to vulnerabilities and functionality issues.
What is the biggest challenge in cybersecurity?
The biggest challenge in the field is a lack of understanding about the business enablement function of cybersecurity teams. The benefits achieved via cybersecurity help businesses thrive and protect their customers by ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
Singapore, Singapore
Member since November 8, 2022
About the author
Ilia is a cybersecurity professional and developer with wide-ranging experience in the government, defense, manufacturing, and finance sectors. A former cloud security architect at Hewlett Packard Enterprise, he now advises executive clients on planning, prioritizing, and executing strategic security initiatives.
Previous Role
Senior Security ConsultantPREVIOUSLY AT