Hire Data Engineers
Hire the Top 3% of Freelance Data Engineers
Hire vetted data engineers on demand. Leading companies choose data engineering freelancers from Toptal for their most important development projects.
No-Risk Trial, Pay Only If Satisfied.
Hire Freelance Data Engineers
Yi Sheng Chan
Yi is currently working at Apple as a software engineer, building a platform and framework for training machine learning models on hundreds of millions of Apple devices in a privacy-preserving way. He has designed and built scalable ML systems and data infrastructure in cloud environments since 2014, and his expertise spans DevOps, ML, data engineering, both batch and streaming, and back-end web services. Yi's strongest skill is Python, Java, Spark, and SQL, coupled with good ML knowledge.
Show MoreAnthony Baxter
Anthony is an analytical and resourceful leader with over 25 years of experience in data engineering, database development, and process design and development. He has deep experience in the financial services industry and a keen ability to understand business and data requirements and customize value‐added applications. He's known for his expert skills in operations and risk management. Anthony is poised and intellectually curious, with executive-level written and verbal communication skills.
Show MoreAsha Asha
Asha is a Microsoft Power BI developer in Microsoft Business Intelligence (MSBI) with over five years of experience. She has hands-on data engineering expertise and has worked with many clients in different industries, including retail, banking, and service providers. Asha is experienced in Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Power BI, SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS), and SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) reporting.
Show MoreDmitry Foshin
Dmitry is a seasoned senior lead data engineer with 12 years of experience in IT and seven years of hands-on expertise in Azure, Databricks, SQL, and Python. Known for leading a globally distributed team of data and BI engineers, he brings a strategic mindset and technical depth to deliver scalable, high-impact data solutions. Clients value Dmitry's ability to turn complex data challenges into clear, actionable results.
Show MoreKrishna Inapurapu
With 15+ years of experience in the banking and automobile industries, Krishna specializes in designing and delivering enterprise-grade solutions using Java, Spring, and Azure data engineering. His expertise lies in architecting scalable, secure, and high-performance data infrastructures that drive innovation and operational efficiency in complex, regulated environments. Krishna excels in leveraging technology to solve challenging problems and enhance business outcomes.
Show MoreKhalid Amin
Khalid is a seasoned data professional with 25 years of industry experience. His expertise includes data architecture, data engineering, modern data warehousing, big data, and analytics. Khalid is experienced in Microsoft Azure and Fabric, Snowflake Cloud Data Platform, Neo4j/graph databases, and GenAI. Additionally, he is skilled with SQL Server and Oracle database technologies. Khalid can speak fluently in English and is a true team player.
Show MoreSachin Sharma
Sachin is a senior developer and AWS Certified Solutions Architect with expertise in data engineering, back-end API development, and DevOps. He has nearly a decade of experience working in Python, PySpark, and cloud environments, particularly AWS, and exposure to DevOps tools like Terraform, CI/CD, and Docker. Sachin is a results-driven professional, always ready to leverage his technical and management skills for upcoming opportunities.
Show MoreMike Sukmanowsky
Mike is a senior technologist with over a decade of experience building and scaling products. Over the past ten years, he has specialized in data engineering, full-stack web development, and product management. Mike is a natural problem solver capable of mastering complex subjects quickly and focusing on delivering real value.
Show MoreGunbilegt Byambadorj
Gunbilegt is a data engineer with 10+ years of industry experience in software, web, and database development. He specializes in building data warehouses, pipelines, and models using SQL, Python, C#, Spark, Hadoop, and .NET. Gunbilegt has worked in oil and gas, minerals and mining, telecommunications, CRM, and eCommerce. He is currently a Hadoop developer with Tata Consultancy Services, and his industry experience is backed by a master's degree in information technology.
Show MoreAmit Jain
Amit is a technology professional with over 21 years of hands-on experience in the architecture, design, build, and implementation of data platforms, transactional systems, and analytics solutions for global Fortune 500 companies. He has worked across banking, insurance, telecom, gaming and attractions, government, B2B eCommerce, life sciences, and higher education industries.
Show MoreHassan Bin Zaheer
Hassan is a professionally qualified developer with over ten years of overall industry experience in software engineering, data architecture, data warehousing, ETL/ELT, feature engineering, database optimization, business intelligence, and consulting. He loves using different tools and technologies, including AWS, Snowflake, SQL databases, Python, Apache software, Docker, and GitLab. With his experience and determination, Hassan will be a great asset to any team.
Show MoreDiscover More Data Engineers in the Toptal Network
Start HiringA Hiring Guide
Guide to Hiring a Great Data Engineer
Data engineers are experts who design, develop, and maintain data systems. This guide to hiring data engineers features best practices, job description tips, and interview questions and answers that will help you identify the best candidates for your company.
Read Hiring Guide... allows corporations to quickly assemble teams that have the right skills for specific projects.

Despite accelerating demand for coders, Toptal prides itself on almost Ivy League-level vetting.









How to Hire Data Engineers Through Toptal
Talk to One of Our Client Advisors
Work With Hand-selected Talent
The Right Fit, Guaranteed
EXCEPTIONAL TALENT
How We Source the Top 3% of Data Engineers
Our name “Toptal” comes from Top Talent—meaning we constantly strive to find and work with the best from around the world. Our rigorous screening process identifies experts in their domains who have passion and drive.
Of the thousands of applications Toptal sees each month, typically fewer than 3% are accepted.
Capabilities of Data Engineers
Data engineers specialize in designing, building, and maintaining robust data infrastructures that help companies unlock the full value of available data. Utilizing tools like Apache Airflow, dbt, and Snowflake, they develop scalable ETL/ELT pipelines, integrate diverse data sources, and uphold high standards for data quality and regulatory compliance. Toptal’s data engineers bring deep expertise in data modeling, real-time processing, and close collaboration with analytics teams to deliver actionable insights and support informed decision-making.
ETL/ELT Pipeline Development
Data Warehouse Architecture
Data Source Integration
Data Cleaning and Transformation
Data Quality Assurance
Data Modeling and Schema Design
Real-time Data Processing
Database Performance Optimization
Data Security and Compliance
Collaboration With Analytics Teams
Find the Right Talent for Every Project
Senior Data Engineers
Dedicated Data Engineers
Offshore Data Engineers
Remote Data Engineers
FAQs
The cost associated with hiring a data engineer depends on various factors, including preferred talent location, complexity and size of the project you’re hiring for, seniority, engagement commitment (hourly, part-time, or full-time), and more. In the US, for example, Glassdoor’s reported average total annual pay for data engineers is $120,000 - $198,000 as of March 2024. With Toptal, you can speak with an expert talent matcher who will help you understand the cost of talent with the right skills and seniority level for your needs. To get started, schedule a call with us — it’s free, and there’s no obligation to hire with Toptal.
Data engineers are not only in demand, the demand is rising rapidly. Informatica tells us that in 2023, two-thirds of polled respondents already use data engineering capabilities, with another 20% planning to implement data engineering tools in the coming year. Moreover, 39% of respondents find data engineering to be of critical importance, up from 32% in 2022.
Look for and evaluate the following qualities in the candidates you review for your data engineering project:
Technical expertise – Choose a Data engineer with a strong understanding of data architecture, database design, data warehousing, and big data technologies. They should be proficient in one or more programming languages, such as Python, SQL, or Java, and have experience with data processing frameworks like Spark or Flink.
Problem-solving skills – A Data engineer must be able to identify, analyze, and solve complex problems related to data storage, processing, and analysis. Look for someone with a strong track record of delivering solutions to challenging data problems.
Communication skills – A talented Data engineer effectively communicates with stakeholders, including business leaders, data scientists, and developers. They must understand their project’s needs and clearly explain technical concepts using simple terms.
Presentation skills – A talented Data engineer is able to present insights accurately in a coherent format, communicating in a clear and engaging manner.
Collaboration skills – A data engineering project often involves collaboration with cross-functional teams, so look for a team player who works well with others.
Relevant experience – Consider the relevance and compatibility of a developer’s previous work with your industry’s domains, data types, and technologies.
Cultural fit – It’s important to find a Data engineer who aligns well with your company’s culture, embracing the organization’s beliefs, values, and attitudes.
At Toptal, we thoroughly screen our data engineers to ensure we only match you with the highest caliber of talent. Of the more than 200,000 people who apply to join the Toptal network each year, fewer than 3% make the cut.
In addition to screening for industry-leading expertise, we also assess candidates’ language and interpersonal skills to ensure that you have a smooth working relationship.
When you hire data engineers with Toptal, you’ll always work with world-class, custom-matched data engineers ready to help you achieve your goals.
The main challenges in data engineering involve collecting, storing, transforming, processing, and analyzing large amounts of data. A Data engineer is responsible for building powerful ETL/ELT processes, ensuring optimal performance, data security, data scalability, data governance, data consistency, and data integrity. The most popular languages used for data engineering are SQL, PL/SQL, and Python.
We make sure that each engagement between you and your data engineer begins with a trial period of up to two weeks. This means that you have time to confirm the engagement will be successful. If you’re completely satisfied with the results, we’ll bill you for the time and continue the engagement for as long as you’d like. If you’re not completely satisfied, you won’t be billed. From there, we can either part ways, or we can provide you with another data engineer who may be a better fit and with whom we will begin a second, no-risk trial.
To hire the right data engineer, it’s important to evaluate a candidate’s experience, technical skills, and communication skills. You’ll also want to consider the fit with your particular industry, company, and project. Toptal’s rigorous screening process ensures that every member of our network has excellent experience and skills, and our team will match you with the perfect data engineers for your project.
You can hire data engineers on an hourly, part-time, or full-time basis. Toptal can also manage the entire project from end-to-end with our Managed Delivery offering. Whether you hire a data engineer for a full- or part-time position, you’ll have the control and flexibility to scale your team up or down as your needs evolve. Our data engineers can fully integrate into your existing team for a seamless working experience.
Typically, you can hire data engineers with Toptal in about 48 hours. For larger teams of talent or Managed Delivery, timelines may vary. Our talent matchers are highly skilled in the same fields they’re matching in—they’re not recruiters or HR reps. They’ll work with you to understand your goals, technical needs, and team dynamics, and match you with ideal candidates from our vetted global talent network.
Once you select your data engineer, you’ll have a no-risk trial period to ensure they’re the perfect fit. Our matching process has a 98% trial-to-hire rate, so you can rest assured that you’re getting the best fit every time.
How to Hire Data Engineers
Tetyana is an AI expert who has served as a founder, chief data scientist, and consultant for clients in several countries. She has worked on projects for large companies like MultiChoice Group and Control Risks in industries including energy, government, education, and biotechnology. Tetyana has built systems for finance and accounting purposes, ML-powered NLP, forecasting, and anomaly detection.
Previously at

Demand for Data Engineers Predicted to Rise With Exponential Growth
Data engineering is a discipline with a rapidly growing demand for qualified professionals. IDC, the International Data Corporation, reports on the exponential growth in the overall volume of data worldwide and predicts that, by 2025, the Global DataSphere forecast will reach 175 zettabytes of data—more than five times the 33 zettabytes recorded in 2018.
With increasing data use comes the need for reliable, experienced data engineers. According to Informatica’s 2023 data engineering market survey, 65% of respondents indicate they are already using data engineering capabilities within their organizations. Another 20% of respondents have plans to implement data engineering tools within the next 12 months. With so many businesses competing for the best candidates, finding a top-notch data engineer becomes challenging.
This hiring guide streamlines the hiring process by presenting the essential attributes that define top-notch data engineers. Discover how to identify applicants who align with your project needs. Gain insights into what makes an effective job description and learn strategies for navigating the interview and assessment phases, ensuring a successful hire.
What attributes distinguish quality Data Engineers from others?
A quality data engineer is responsible for tasks beyond the day-to-day processing of data. This skilled specialist also oversees the implementation of suitable data architectures and the maintenance of the data that flows within them.
To distinguish a quality data professional from others, look for candidates who possess considerable experience with architectural design and cost and performance management of data systems. Additionally, when working on enterprise-scale solutions, you may want an engineer who can serve as the point of contact for communication with stakeholders, clarifying the business meaning of the data, as well as maintaining documentation and data catalogs.
What does a Data Engineer do for a business?
With the sheer amount of data being processed every day, data engineers are being called upon to ensure that data-driven operations run smoothly and securely. Data engineers are involved throughout the entire data processing life cycle, from ingestion and cleaning to analysis and reporting. They are responsible for ensuring a secure, efficient, and reliable flow of data. A data engineer can design an optimal infrastructure for processing data to enable AI/ML engineers and data scientists to glean business insights.
Hiring a skilled data engineer to design and maintain data pipelines can lead to more reliable operations, more efficient data processing, and cost savings. Faster and more accurate insights enable an organization to be more agile, with improved response times to changes in business, environment, and/or consumer sentiment. A dedicated data engineer is essential for an organization that deals with big data, complex data management, or private customer data.
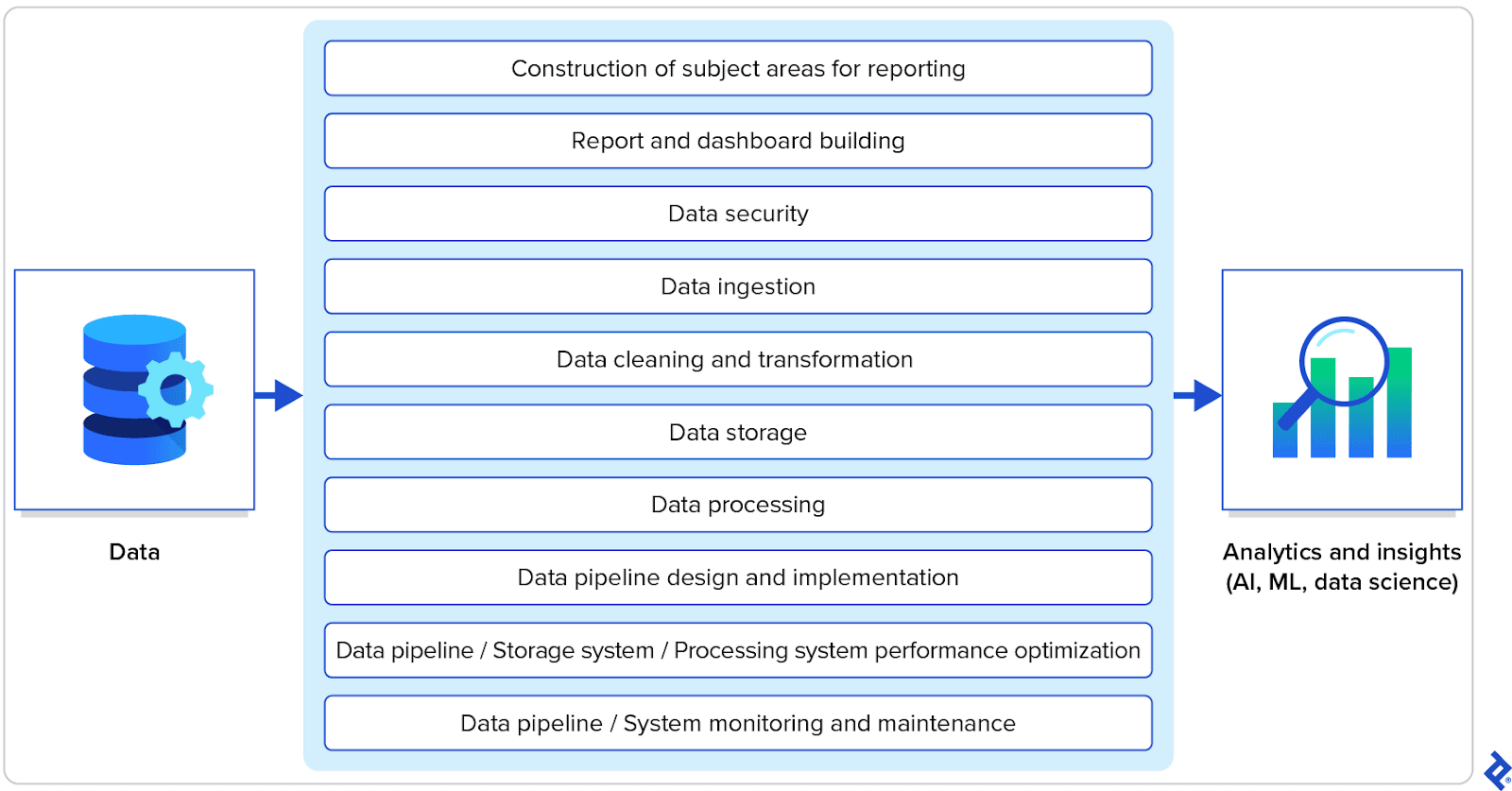
What skills should a data engineer have?
The day-to-day responsibilities of a data engineer require a multifaceted skill set that blends technical and problem-solving prowess with an in-depth understanding of the entire data processing life cycle. Experienced data engineers will have expertise in the following areas:
Modeling data for business-specific reporting – Integrates measures, dimensions, and metadata to reflect various—and possibly conflicting—ways that users may perceive that data. Data engineers need to be capable of building models that align with your unique business needs, delivering more accurate insights and avoiding misrepresentation.
Report and dashboard building – Presents data in a coherent, unified manner that tells an accurate story. From data visualization best practices to interactivity, connectivity, and drilling down to the details, data engineers are often responsible for presenting data.
Data pipeline design, optimization, and maintenance – Designs optimized pipelines, storage systems, and processing systems to ensure that data is moved and processed reliably and efficiently from source to destination. This often involves integrating data across systems: combining data from multiple disparate sources and ensuring it is unified and accessible across different systems or applications. Resource allocation should be optimized to minimize costs and improve processing times. Monitoring and maintenance should also be prioritized to minimize downtime and maximize data quality and availability.
Data ingestion, cleaning, and transformation – Designs and implements data ingestion pipelines to ensure that data from various source systems and formats (such as REST APIs, JSONs, Excel spreadsheets, favorite flavors of SQL, and big data key-value pairs) is successfully delivered into a central database and made available for analysis. Additionally, all data is transformed into a usable format, in a unified view, ideal for generating insights. Irrelevant, incomplete, or incorrect data is removed, and metadata is applied as appropriate. Data engineers bridge the gap between different data sources, facilitating reliable data access and efficient analysis.
Data storage and processing – Designs and maintains data warehouses, data lakes, and other data storage systems. Modern data analysis often involves data sets containing vast amounts of data, which require specialized handling. Choosing the right storage system is essential for scalability and performance. Data engineers who have expertise in working the different types of storage systems, as well as with handling large data sets, can deliver insights faster and more reliably, improving the company’s agility and responsiveness.
Data security – Applies security to data when building processes and flows. Security is commonly achieved by limiting which aspects of the data, forms, and analysis are presented to which users. Security also entails the anonymization of specific data, maintenance of access logs, and proactive monitoring. In order to protect the company from data breaches, security should be a high priority on a data engineer’s skill list.
How can you identify the ideal Data Engineer for you?
A data engineer is a multifaceted professional who combines the skills of a programmer, architect, and DevOps engineer with a deep understanding of data structures and data processing algorithms. Different types of businesses have distinct criteria for and diverse expectations of a quality data engineer, so a developer who suits one company may not be as good a fit for another. When choosing your data engineer, you should consider the required expertise level and project-specific skills.
What is the difference between a junior and senior data engineer?
To fill a junior position, look for candidates who have taken a data engineering course or a course in a related discipline, such as data science, software engineering, or database administration. Candidates should have relevant experience in writing ETL/ELT, automating pipelines, and working with your selected database technologies and/or data warehouse / data lake solutions.
To fill a senior position, look at expert data engineers with a wide range of experience, for example, an engineer who started out as a database administrator, SQL developer, or data scientist and later turned into a data engineer. Candidates should have an understanding of your technology and business processes—from customer-facing applications, accounting, ERP, and CRM systems to data science/machine learning pipelines, as well as data visualization. They should be able to use the extracted analytics to build interactive dashboards and reports.
What complementary technology and technical skills are essential for a data engineer?
Consider the following complementary data engineering skills and how they might align with your company’s needs now—or in the future:
Programming languages – Proficiency in at least one programming language is a must for a data engineer. Python and Java are the most commonly used programming languages for data engineering, though some areas of data engineering may require proficiency with C, C++, or another language. A data engineer should be familiar with the programming languages and libraries that support a business’s specialized data, such as medical or space imagery, or genetic data sets.
Database management – Knowledge of database management systems (DBMS) such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Cassandra, is essential for data engineers. They should also be proficient in SQL for data retrieval and manipulation. In addition, a solid understanding of data warehousing and modern warehousing products, such as Snowflake and Redshift, is a must.
Cloud computing – Many organizations use the cloud to store and process large amounts of data. Not only is experience with cloud computing platforms such as AWS, GCP, and Azure important for data engineers, they must also understand the pros and cons of working with the various clouds. For a company that uses or plans to use AI and ML, the data engineer must also understand the integration of generic clouds with cloud-based AI/ML solutions such as H2O.ai, RapidMiner, or Databricks.
Distributed systems – Knowledge of distributed systems and how to design, build, and maintain distributed data pipelines is crucial for a data engineer. A data engineer must understand how to use tools such as Kafka, Spark, and Apache Flink to design fault-tolerant systems and ensure data consistency across the system parts.
Automation – A data engineer uses tools such as Apache Airflow and Jenkins to automate, monitor, and troubleshoot repetitive tasks, such as data ingestion and data processing, ensuring efficiency and scalability.
What is the difference between data engineering and data science?
With the emergence of new professional job titles whose names sound alike, it can be confusing to distinguish the differences between the two. Understanding the types of projects that each professional is best suited for is a prerequisite to starting the hiring process.
Data engineering is the practice of preparing, processing, and managing data for analysis. It includes tasks such as data extraction, cleaning, transformation, and storage. A data engineer is responsible for building and maintaining the infrastructure that supports data science projects, such as data pipelines, data warehouses, and data lakes.
Data science, in turn, is the practice of using data and statistical models to extract insights and make informed decisions based on the data. Data scientists are responsible for defining the questions to be answered by the data, selecting the appropriate data sets and models, and interpreting the results of their analyses. They also communicate their findings to stakeholders.
How to Write a Data Engineer Job Description for Your Project
Data engineering positions span a variety of responsibilities and levels of experience. Begin your job post with a well-crafted title that thoughtfully describes the role, incorporating the level of experience necessary to fulfill the job, as well as the company’s stance on remote work and, if possible, the expected length of engagement. For example, the title “Hybrid position: Senior data engineer, 6 months” effectively features these key aspects.
Next, describe your current data ecosystem and the tasks the data engineer will be performing. Name the data management systems you use and specify whether:
- You have a data warehouse or a data lake.
- Your data systems are integrated.
- You need a data engineer who will maintain existing pipelines and add new ones as needed.
- You are planning a major overhaul of your data system, such as moving to the cloud, creating a new data warehouse or data lake, replacing a warehouse with a data lake, or changing the organizational process for the establishment of a data mesh.
Your clear description of the position goes a long way toward helping candidates establish realistic expectations of the job.
What are the most important Data Engineer interview questions?
Effective interviews are about asking the right questions. Following are some questions and interview prompts to help you test your candidates’ knowledge and understand their approaches to data engineering.
What does pipeline development involve?
This question gives insight into each candidate’s knowledge of a data engineer’s core responsibilities and skills. Pipeline development is a fundamental aspect of the job and involves automating the cleaning, extraction, transformation, and loading of data. A good data pipeline will also include quality checks and error alerts. Creating documentation and data catalogs is considered to be an aspect of pipeline development.
What is data cleaning, and how is it implemented?
Data cleaning—also known as data scrubbing—is an important step in any data pipeline, and all candidates should be familiar with its tools and techniques. Data cleaning refers to deduplicating data, removing meaningless data, and filling in any missing values. Cleaning can be automated in a pipeline through which data passes, coming out cleaned or sanitized. A pipeline typically finds and removes outliers, validates the data, secures and/or anonymizes the data (e.g., removing credit card numbers), and corrects recurring errors (e.g., replacing instances of two spaces with one space within text data). Some of the popular data cleaning tools include OpenRefine, Alteryx Designer Cloud, and the Pandas Profiling library.
How does data warehousing work?
Data warehousing is a fundamental concept in data engineering, and good data engineers should understand its basic principles. A data warehouse is a software system that maintains a central data repository. Specifically designed for efficient data analysis, reporting, and decision-making, a data warehouse typically uses a relational database management system as its underlying technology. Data is collected from one or more sources (such as a transactional database, operational data store, or reference data) and, after cleaning and transformation, moved to a central repository.
What is the difference between a data warehouse and a data lake?
Because data engineers are frequently asked to choose between a data warehouse and data lake, it is important for candidates to have an understanding of the differences. A data warehouse consists of highly structured data that is easy to analyze, while a data lake contains unstructured data that a data scientist must pore over to create meaningful analyses. Candidates should also mention the importance of different factors, such as data volume, processing needs, and access patterns, when choosing between a data warehouse and a data lake.
Cite some of the best practices in data engineering.
This question assesses each candidate’s understanding of good data engineering practices, as well as giving insight into their experience and what areas they prioritize. Each candidate’s response will give you an idea of their overall approach to data engineering. While specific practices will vary based on the project’s needs, the following guidelines are commonly regarded as best practices for data engineering:
- Create simple functions designed to perform a single task.
- Generate data lineage; maintain a data catalog with a history of any data transformation from raw data.
- Choose and install compatible and nonredundant tools.
- Secure data by implementing access control—covering granular permissions for individual data elements and row-level access, as well as controlling access to complete reports and dashboards. Add a usage tracking log and store passwords and access keys in specialized security stores.
- Establish and follow naming conventions.
- Develop parameterizable pipelines.
What is a relational database management system?
A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a software system that organizes and manages data using structured tables for efficient manipulation. This system typically involves storage, retrieval, querying, and updating. Objects such as tables and views can be linked to one another, with a schema showing the manner in which they are connected. Most data engineers work with relational databases like SQL Server, PostgreSQL, or Oracle Database. Each candidate’s response can reveal their experience with using and managing relational databases and can lead to a discussion about specific platforms.
Why do companies hire Data Engineers?
With the explosion in data production and the opportunities offered by effective data analysis, the need for data engineers is self-evident. A quality data engineer can help your company build an efficient data ecosystem and simplify the work of your AI/ML engineers and data scientists.
An expert data engineer is one who is qualified to advise and choose the tools and frameworks that best serve a company. By implementing such recommendations, a company is positioned to enjoy significant savings in time and costs, as well as a boost in its competitive edge. Having a qualified data engineer on hand provides assurance that the company’s data analytics engineers can operate efficiently and effectively which, in turn, frees the company to serve their customers reliably.
The technical content presented in this article was reviewed by Boris Mihajlovic.
Featured Toptal Data Engineering Publications
Top Data Engineers Are in High Demand.