Customer Journey Maps: What They Are and How to Build One
Customer journey maps are a visual storytelling tool used to help designers empathize with users and identify actionable opportunities for providing a better user experience.
Customer journey maps are a visual storytelling tool used to help designers empathize with users and identify actionable opportunities for providing a better user experience.
Bree’s a passionate designer and problem-solver with 10+ years experience in product and UXUI design for web and native mobile applications.
Expertise
PREVIOUSLY AT

When a customer uses a company’s products and services to achieve a goal or need, they are going on a journey from point A to point Z. A customer journey map charts the path a user takes from the beginning of this journey to the satisfaction of that need.
Mapping out the customer journey is an effective way to understand what turns a viewer into a long-term, loyal customer. – Kofi Senaya, Director of Product at Clearbridge Mobile
Understanding a user’s needs is the bedrock of great design. User experience and product designers draw upon a range of tools and methods for uncovering the needs of their users and designing a product that meets those needs.
The customer journey map is one such tool to deploy in the early stages of the design process to help empathize with users and identify opportunities for providing a better experience.
What Is a Journey Map?
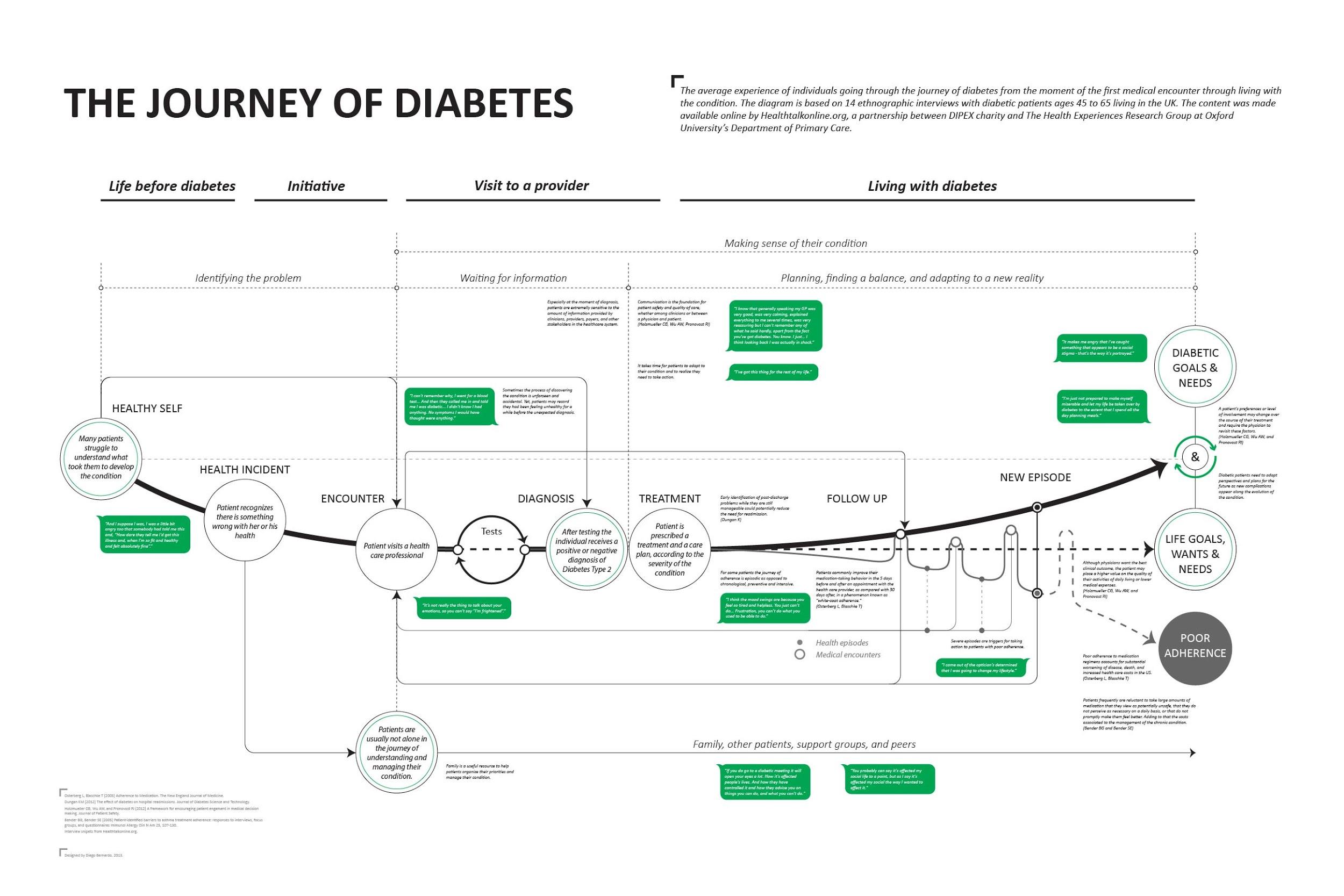
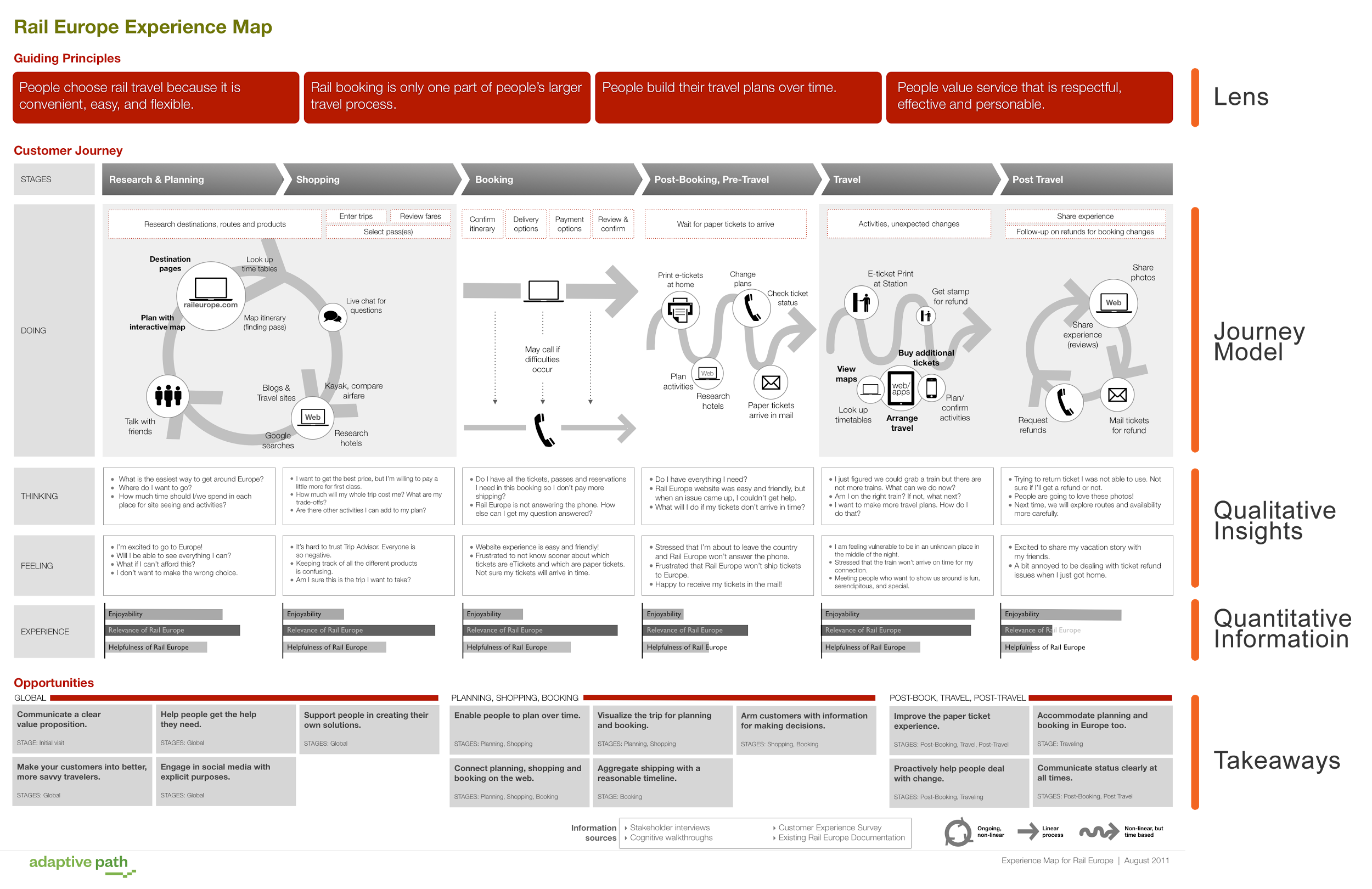
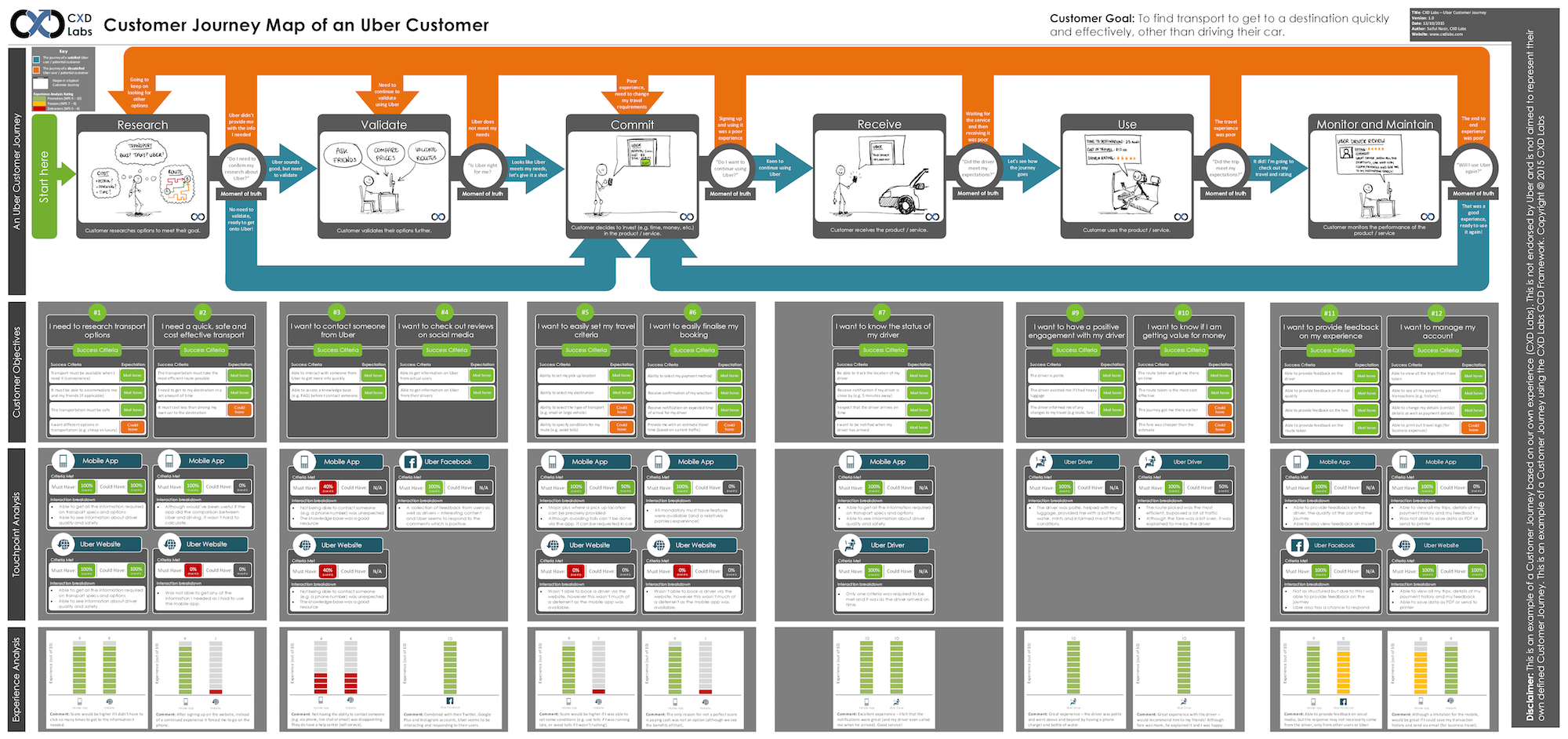
“Journey mapping combines two powerful instruments: storytelling and visualization,” according to Kat Kaplan in When and How to Create Customer Journey Maps. A customer journey map can take a variety of forms, but essentially, it is a visual representation of a customer’s experience with a product or company at various touchpoints over time.
A Customer Journey map is a visual or graphic interpretation of the overall story from an individual’s perspective of their relationship with an organization, service, product or brand, over time and across channels. […] The story is told from the customer’s perspective, but also emphasizes the important intersections between user expectations and business requirements – Megan Grocki at UX Mastery
A customer journey maps help designers and other stakeholders empathize with the needs of their customers, triangulate pain points that their users experience, and identify opportunities for improvement and innovation. Most customer journey maps attempt to track the customer’s potential emotions during the experience: curiosity, confusion, anxiety, frustration, relief, etc.
The quest to understand the target user or customer is not new or specific to the digital landscape. Disney, arguably the masters of great customer experience, began mapping out their customers’ multi-channel engagement—from movies to toys to theme parks—decades ago.
The terms “journey map” and “experience map” are often used interchangeably in the design community, although some designers draw a line between the two terms. As the debate rolls on, it is perhaps less important to debate the distinctions than to focus on the essential goal of mapping out and better understanding the customer journey.
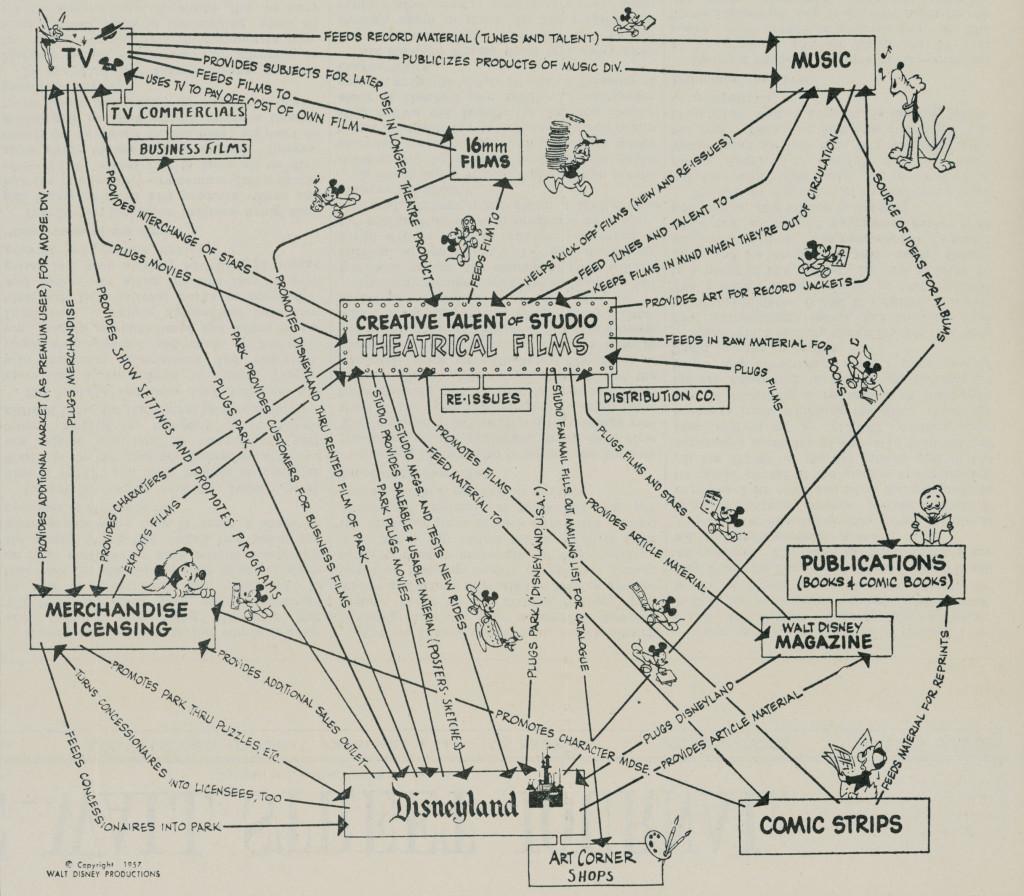
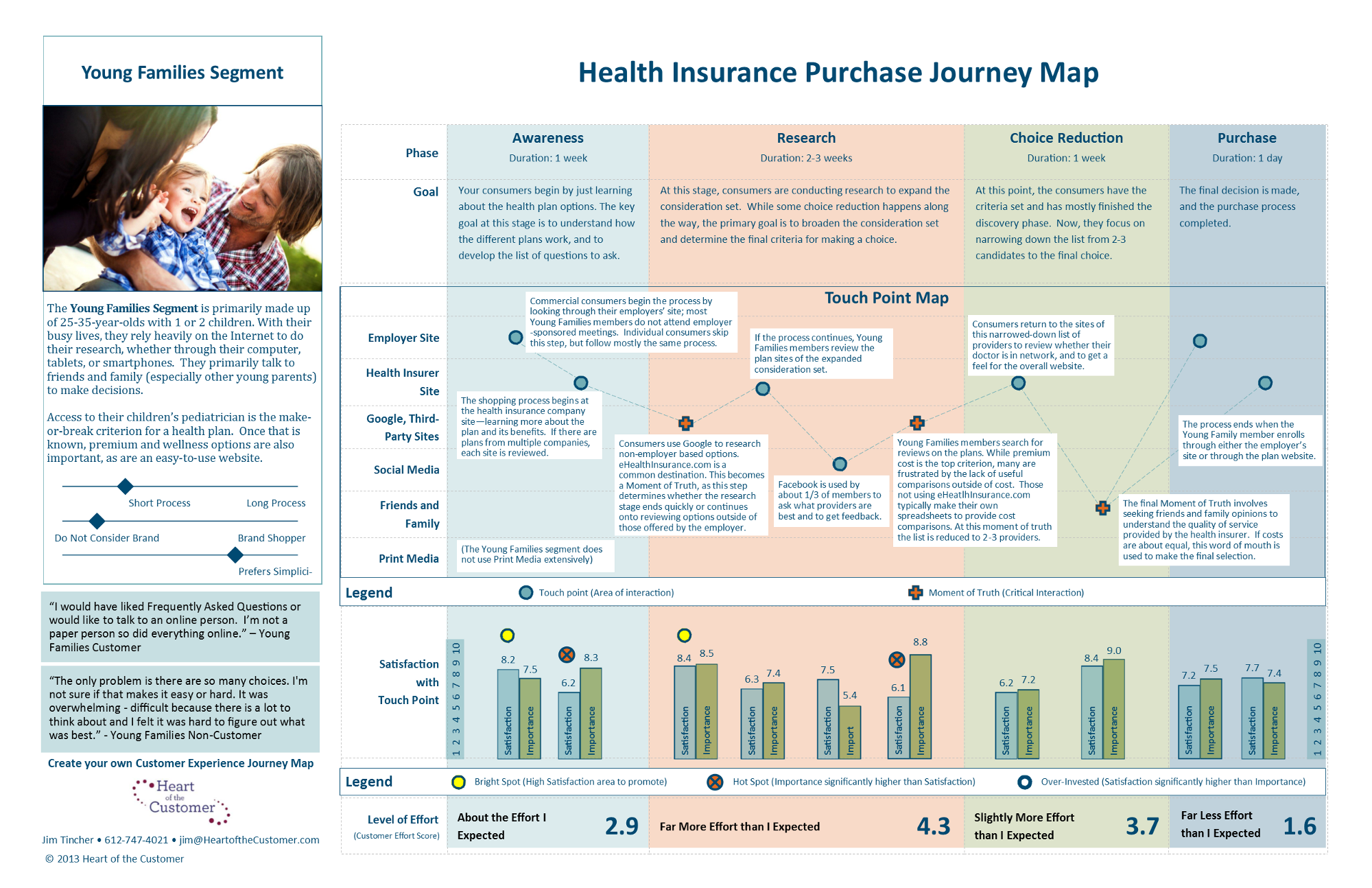
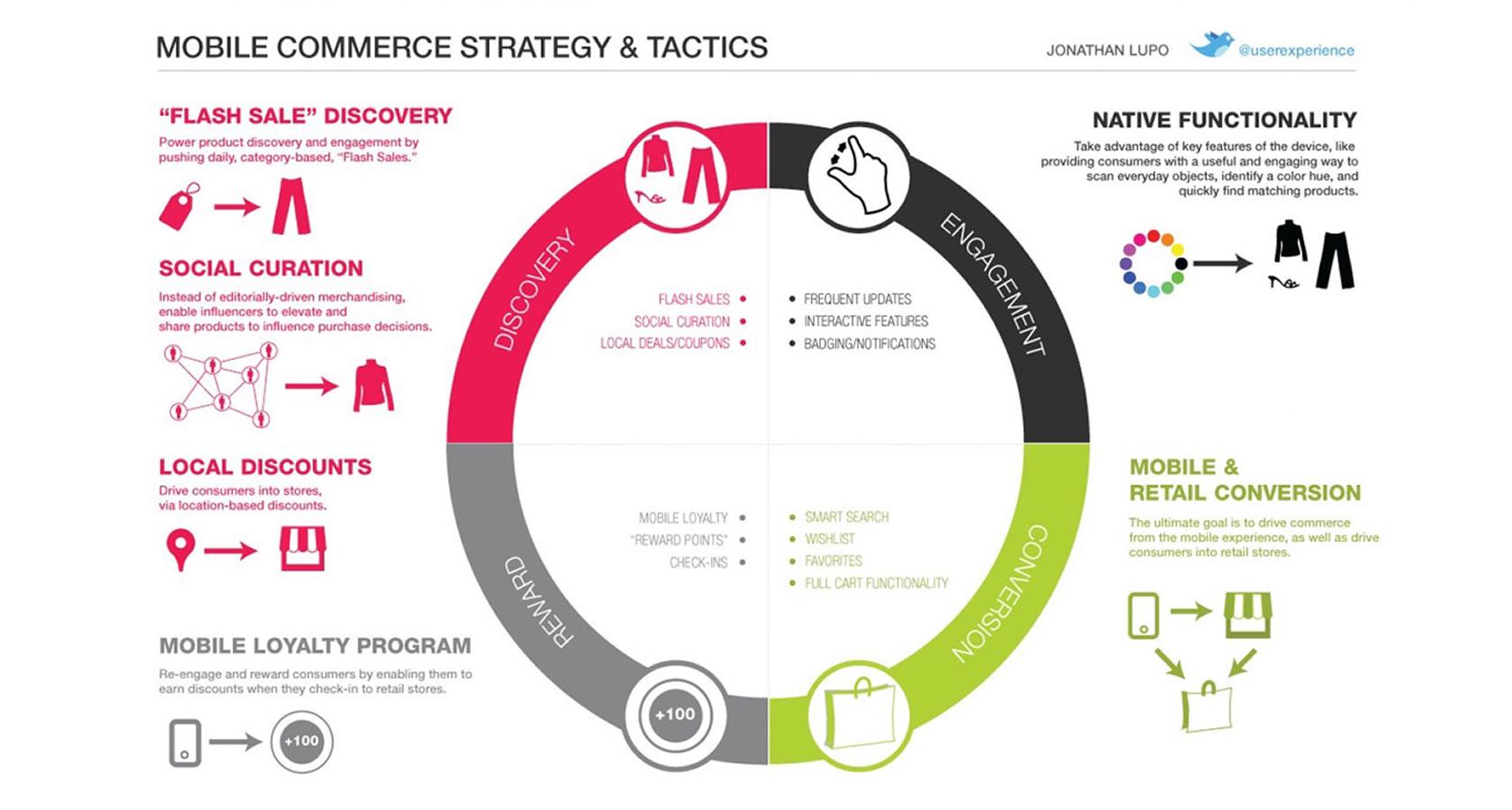
A customer journey map can focus on a single task or experience, such as mapping out a payment flow, or can cover the full life cycle of a customer’s initial engagement and continued retention. A product journey map lays out a customer’s interactions with a particular product.
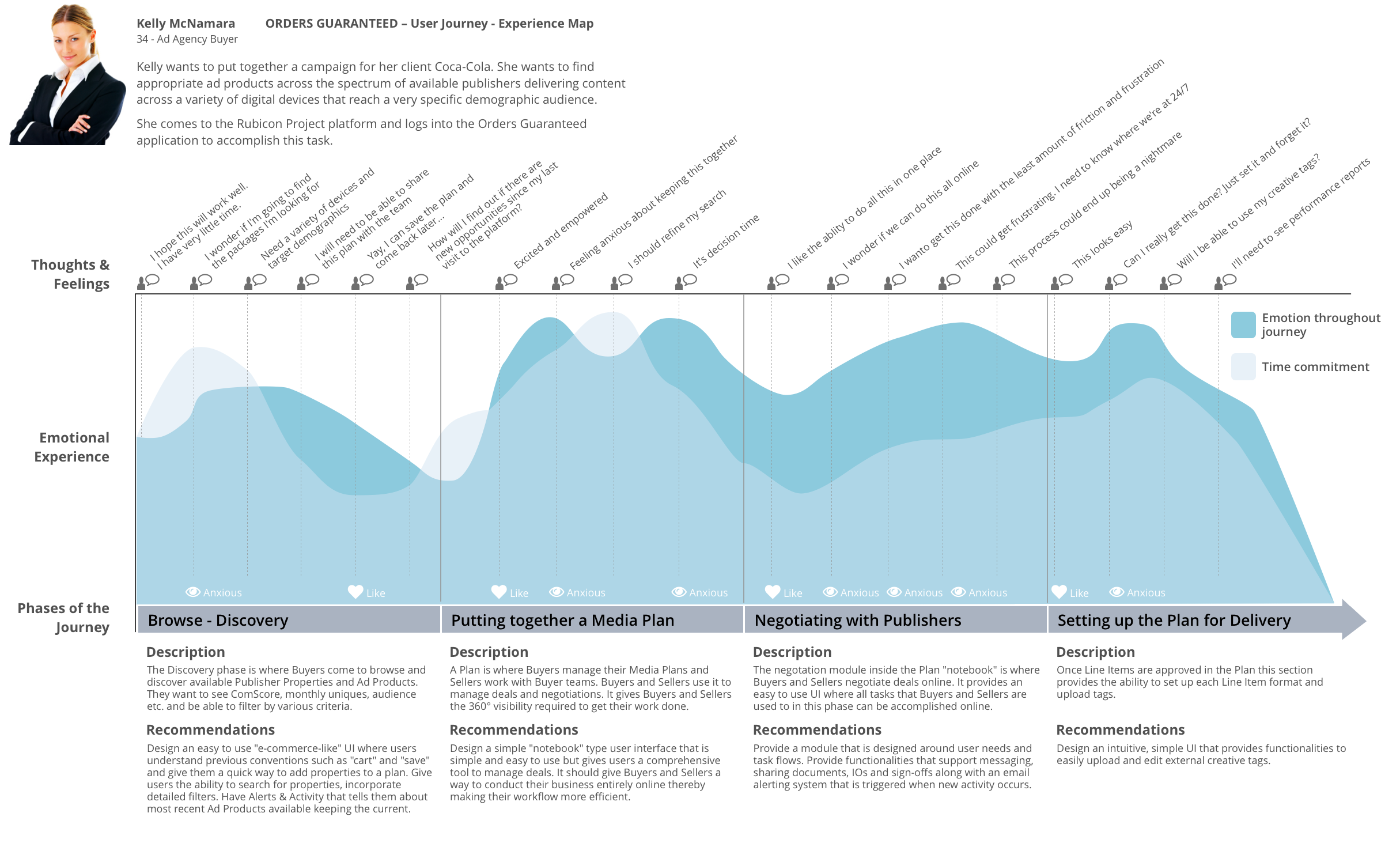
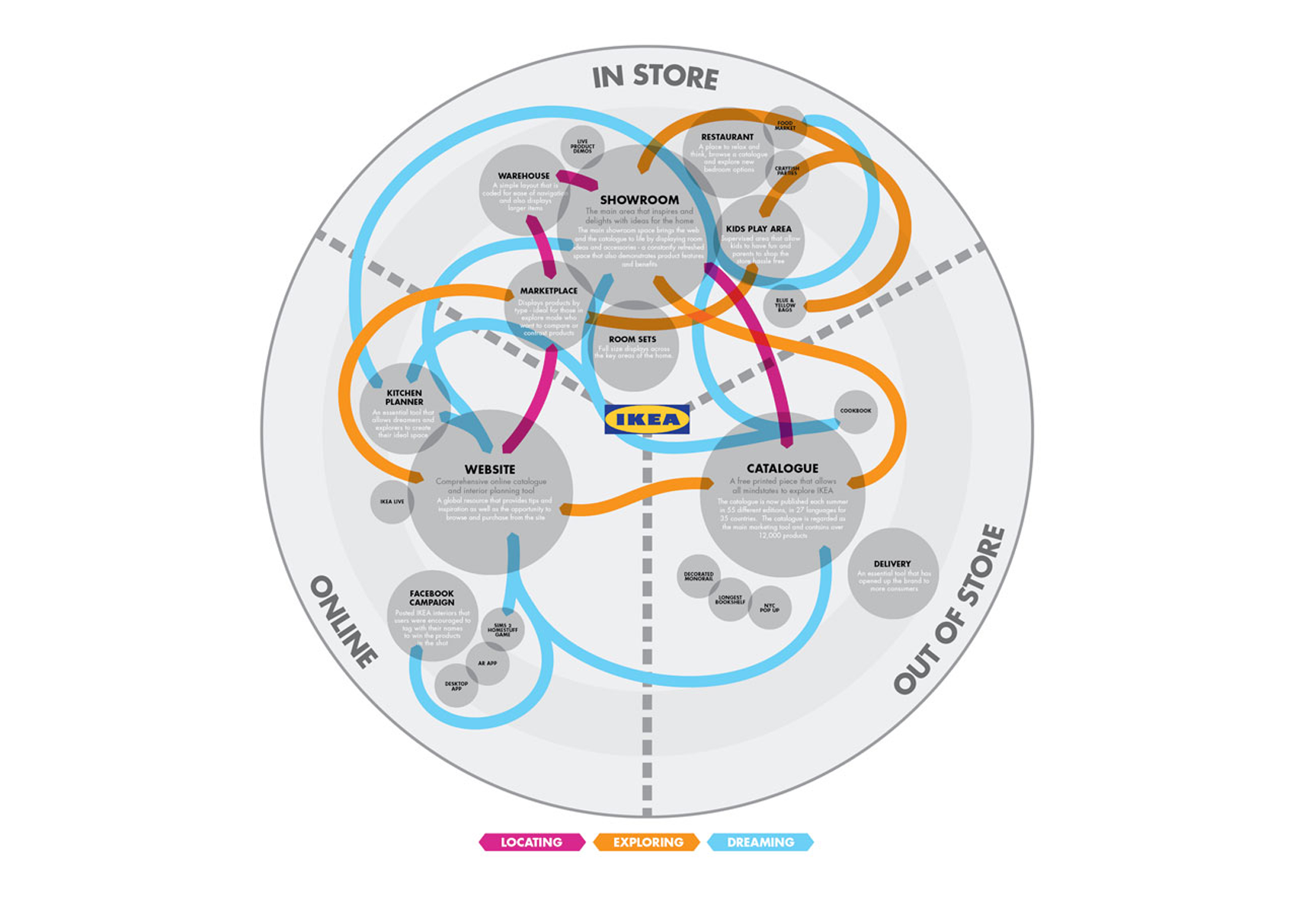
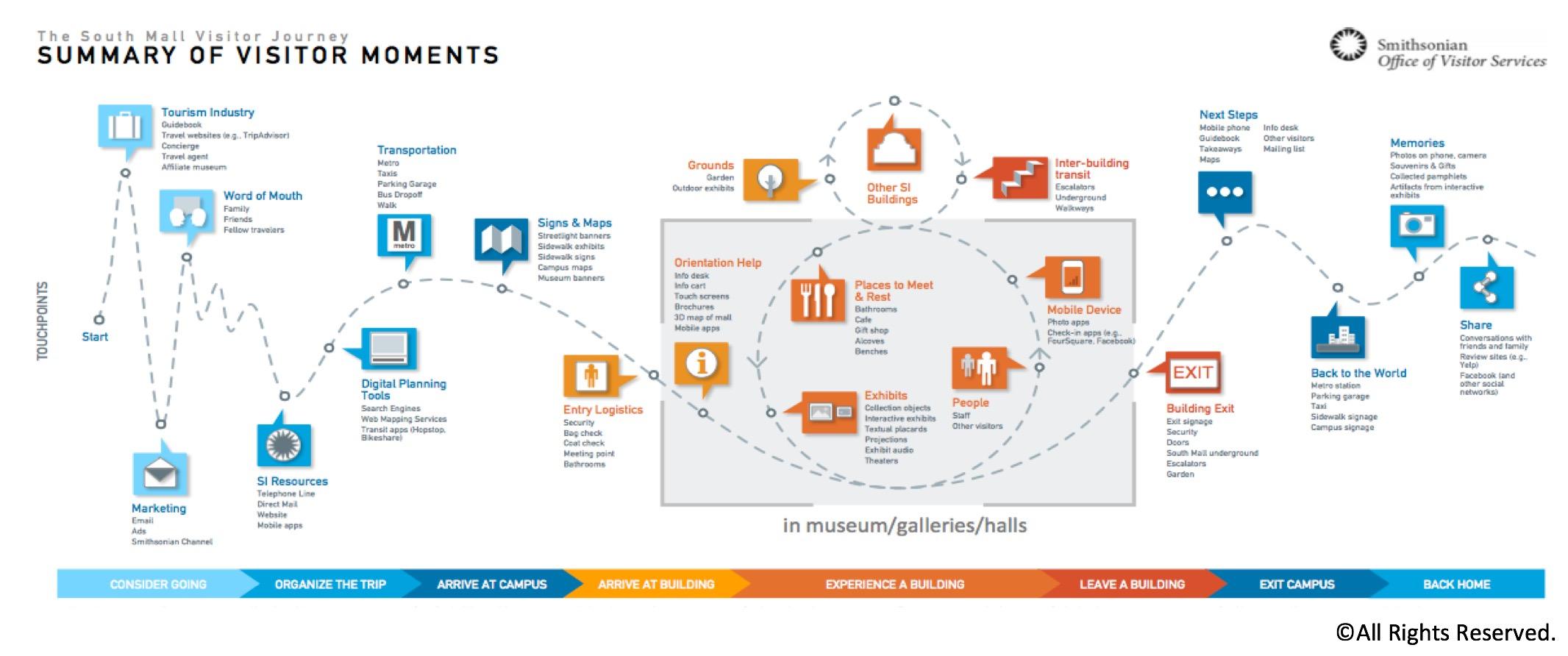
The journey map design may center on a specific feature or app, or it may follow the customer’s experience at each touchpoint across a company’s service ecosystem. If a company relies on multiple channels and various touchpoints for customer service, for example, a map can help identify when best to escalate a customer email to phone support.
User journey maps help designers and stakeholders empathize with a user’s motivations and experiences from point A to Z and beyond. Like any other maps, a customer journey map helps one understand where the customer is and how to help get them where they want to go.
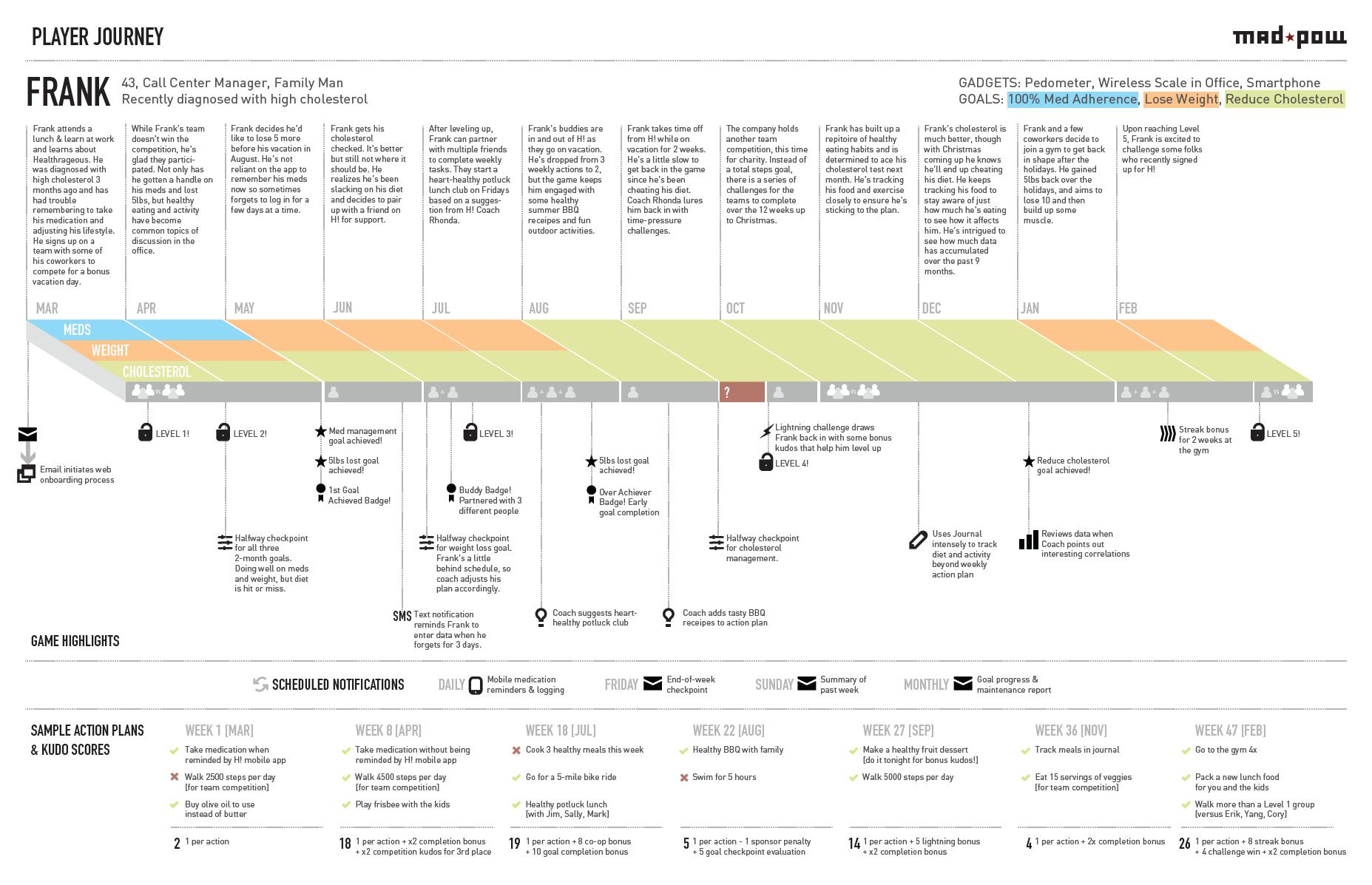
A customer journey map helps designers and stakeholders figure out what questions to ask but does not immediately answer them. One should approach the customer journey mapping process as an act of discovery, where the exercise itself illuminates the path to take.
Since the map is meant to be a catalyst, not a conclusion, the takeaways drive the next phase of the design or strategy by illuminating the journey, and helping to identify the opportunities, pain points, and calls to action. This will depend on what your next steps are, driving strategy or tactical design. – Adam Ramshaw at Genroe
Mapping is an exercise of connecting concepts and data to each other. In the case of customer journey maps, designers should be looking at how the customer’s intent maps to the flow of interaction provided at various touchpoints and seeing more clearly how they are connected or disjointed.
How to Create a Customer Journey Map
Start with User Research
All great design begins with research, whether analytical or anecdotal. The more one knows about a customer and their needs, the more accurate a map will be.
Conducting proper research will help designers avoid basing assumptions about their users on false consensus. “The false-consensus effect refers to people’s tendency to assume that others share their beliefs and will behave similarly in a given context,” according to Raluca Bidiu in You Are Not the User: The False Consensus Effect.
Feedback surveys are direct ways of asking users about their needs and what they’re already doing to meet those needs. User interviews open up the opportunity, not just in order to ask a lot of questions but to also observe what the users are not saying about their needs.
Customers will respond to a product within the framework of completing a particular task. This means the customer journey starts before users even engage with a single product and continues after they leave. Capturing a customer’s perception of their experience relative to their goals and needs informs how a designer can improve upon it.
Customer journey maps then use storytelling and visualization to map out the customer’s experience over time with the product, which aids the design team in identifying actionable opportunities for improving the experience.
Looking at more quantitative analytical data can provide valuable insights into the product’s users as well. For example, is there a significant drop off in user engagement at a particular screen in the subscriber sign-up experience? A clear user journey map might help designers understand what’s happening and if there are any gaps in the overall experience.
There is also great value in conducting competitive and comparative research. Observe how users engage with existing products and solutions. Mapping out a competitor’s customer experience as a story can be far more revealing than looking at a flat feature table.
One should also leverage others in their organization. Anyone who interacts with customers or their feedback should be interviewed: point-of-service providers, customer support specialists, error message report handlers, etc. Getting the other side of the story is a surprisingly effective way of understanding where customers are experiencing confusion or frustration.
Identify the Lens of the Experience
Before one begins mapping out a customer experience, one must define what the question to be examined is. After synthesizing the research, one should be able to understand the scope or timeline of the experience.
Remember that customers are not considering the experience of a company from just one microinteraction; every touchpoint at which they come into contact with someone’s products and services is part of a larger, comprehensive experience.
Does research reveal that customers show high initial satisfaction with a company’s eCommerce site that tapers off after the first transaction? Are customers enjoying a responsive website, but deleting the native app after first launch? How does a company foster loyalty in its publication readers and keep them coming back?
Mapping out the customer journey across each channel helps designers survey and optimize the overall experience. This may even mean looking at how the overall experience involves other platforms and services. For example, an eCommerce experience may begin with a search engine such as Google before the customer even gets to a company’s own website.
To solve for a specific problem or pain point for the customer, it may make sense to focus an experience mapping exercise on that flow. This does not mean, however, that the map can’t be complex—a payment experience for a company that offers both online and in-store shopping can cross multiple channels of service.
Building a map out for each touchpoint segment allows the team to research the component parts that make up the whole story more deeply. Focus the lens on specific segments or points in time of the customer journey while keeping the holistic experience in mind. By mapping out the experience across these channels, one can begin to suss out if the snag is isolated to an online payment processor or is something more systemic.
The Customer Journey Mapping Process
Now that the prep work surveying the landscape has been completed, it is time to draw out the customer journey map. It is advisable to begin by scribbling the basics out on paper before moving into user journey mapping tools like Sketch or Omnigraffle.
Specify the timeline lens and plot out the user’s main goal at the beginning of the customer journey map, and whatever constitutes a success at the end. This does not have to be linear; for example, points in a repeatable experience can be plotted along a circle. Begin to fill in what the high-level steps are that the user is meant to take to get from point A to point Z.
Once the outline is laid out, try to group steps into stages. For example, if a user is trying to book a hotel room, one might group searching activities with browsing activities as the “research” stages of the journey. This will help you further contextualize and link the user’s motivations and actions.
If you’re looking at a multi-channel journey, for instance, you may also want to plot what happens at each of these stages within each channel. How does customer service escalate a service request? How does an online purchase system connect with an in-store return? What are the best ways to guide the user who must initiate a rideshare service with an app, and then later perform further actions to complete their task?
Most journey maps will also try to track a customer’s emotions during each stage of the journey. Refer to research, especially insights from user interviews and customer support calls, to empathize with points of frustration as well as moments of delight in the experience.
Make sure the information included is clear and concise—easily digestible for the team and stakeholders. Refine the map down to the essential so that the insights it highlights are actionable.
Think of the customer journey map as a poster pinned to the office wall. At a glance, people should be able to see the key touchpoints that a user passes through. It should remind them that the customer’s needs must always be at the forefront of their thinking – Paul Boag of Smashing Magazine
The Importance of Customer Journey Maps
The success of a customer journey map can be measured by how well it helps the team identify pain points, as well as opportunities for improvement as it traces the customer’s path from start to finish. A successful map provides an honest assessment of a company’s existing products and services, then helps spark ideas on how the customer’s needs can be better met.
Present the map to the design and development team as well as stakeholders. Look at the map with an honest, analytical eye. Connect customers’ emotions, such as frustration, with the motivations and expectations guiding the user’s actions. Look for gaps between various channels of your business where the experience falls through. Refer back to the customer journey map repeatedly throughout the design process to validate potential solutions.
A journey map is meant to empathize with customers and identify problems and opportunities; not solve them. The customer journey map is a living, ever-evolving map of a customer’s interactions with the products and services a company has to offer. New touchpoints may be created and customer journey designs re-routed as the team iterates, tests, and validates new solutions.
Use a customer journey map to develop better empathy with customers, leverage user research to identify potential pitfalls in the product journey, and guide the team to craft a more cohesive, seamless user experience, whether this experience is focused on one interaction or occurs across multiple channels.
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- E-commerce UX: An Overview of Best Practices (with Infographic)
- The Best UX Designer Portfolios: Inspiring Case Studies and Examples
- Heuristic Principles for Mobile Interfaces
- The Importance of Human-centered Design in Product Design
- Anticipatory Design: How to Create Magical User Experiences
- Voice of the Customer: How to Leverage User Insights for Better UX
Bree Chapin
New York, NY, United States
Member since May 15, 2016
About the author
Bree’s a passionate designer and problem-solver with 10+ years experience in product and UXUI design for web and native mobile applications.
Expertise
PREVIOUSLY AT